Architecture v4
Failover Manager is a high-availability tool that monitors the health of a Postgres streaming replication cluster and verifies failures quickly. When a database failure occurs, Failover Manager can automatically promote a streaming replication standby node into a writable primary node. This capability ensures continued performance and protects against data loss with minimal service interruption.
A Failover Manager cluster is made up of Failover Manager processes that reside on the following hosts on a network:
A primary node is the primary database server that is servicing database clients.
One or more standby nodes are streaming replication servers associated with the primary node.
The witness node confirms assertions of either the primary or a standby in a failover scenario. If, during a failure situation, the primary is in a partition with half or more of the nodes, it stays primary. As such, Failover Manager supports running in a cluster with an even number of agents.
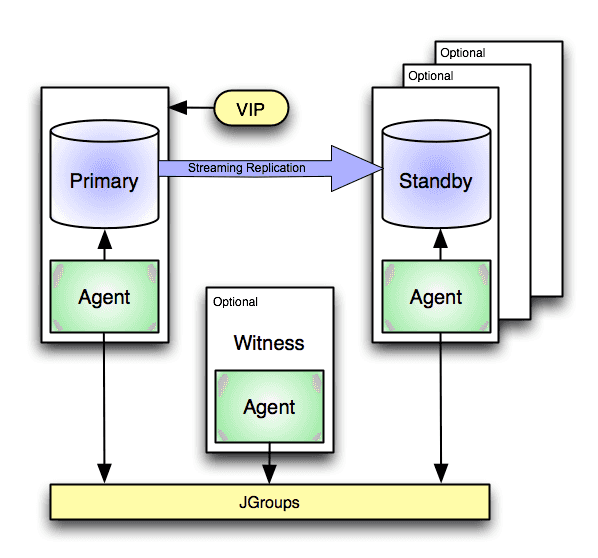
When a non-witness agent starts, it connects to the local database and checks the state of the database:
- If the agent can't reach the database, it starts in idle mode.
- If it finds that the database is in recovery, the agent assumes the role of standby.
- If the database isn't in recovery, the agent assumes the role of primary.
In the event of a failover, Failover Manager attempts to ensure that the promoted standby is the most up-to-date standby in the cluster. Data loss is possible if the standby node is not in sync with the primary node.
JGroups provides technology that allows Failover Manager to create clusters whose member nodes can communicate with each other and detect node failures.
The figure illustrates a Failover Manager cluster that uses a virtual IP address. You can use a load balancer in place of a virtual IP address if you provide your own script to reconfigure the load balancer whenever databases are added or removed. You can also choose to enable native EFM-Pgpool integration for high availability. See Choosing a deployment architecture for more information.