Failover Manager with EDB Pgpool-II v4
Pgpool-II is a popular connection pooler that can provide many capabilities, like read-only traffic load balancing, connection pooling, and running as a clustered proxy. With Failover Manager to manage availability and reconfiguring EDB Pgpool-II to proxy to the correct primary, the setup can deliver high availability in an on-premises setup as well as in a cloud setup.
Failover Manager with EDB Pgpool-II on premises
For an on-premises setup, you can use a VIP to route the traffic to an available EDB Pgpool-II instance. In this setup, the automatic failover of EDB Pgpool-II is disabled, and Failover Manager is configured to manage EDB Pgpool-II.
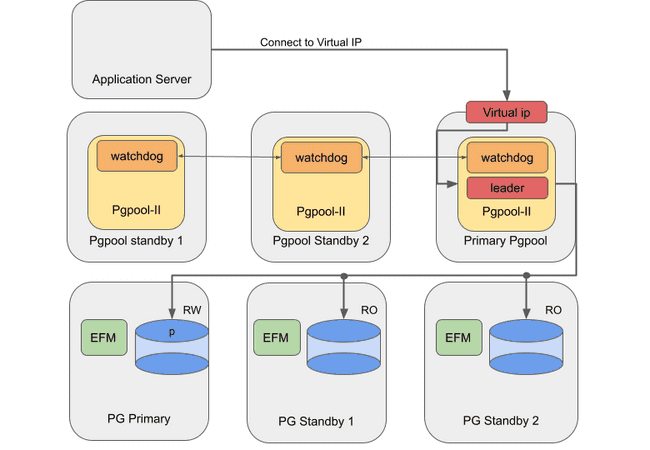
Failover Manager with EDB Pgpool-II in the cloud
For environments with network load balancers (e.g., cloud environments), you can use a network load balancer (NLB) to balance the traffic over all available EDB Pgpool-II instances without requiring a VIP.
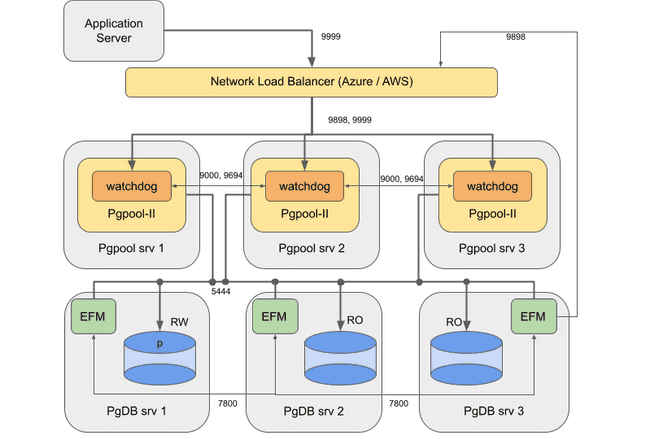
Using Failover Manager with EDB Pgpool-II
Installing
Install and configure Advanced Server database, Failover Manager, and EDB Pgpool-II as follows:
| Systems | Components |
|---|---|
| PgDB server 1, server2, and server 3 | Primary / standby node running Advanced Server 13 and Failover Manager 4.2 |
| EDB Pgpool-II | Pgpool node running EDB Pgpool-II 4.2 in a watchdog configuration. Register these three nodes as targets in the target group. Three is the minimum and is sufficient for most cases. |
EDB does not support this architecture with EDB Pgpool-II and Failover Manager/PostgreSQL running on the same machines for the following reasons:
A restriction with cloud network load balancers doesn't route traffic properly when source and destination reside on the same machines.
In mixed architecture, traffic between Pgpool and Postgres can become unbalanced.
Pgpool and PostgreSQL might compete for resources.
Configuring Failover Manager
Failover Manager can remove failed database nodes from EDB Pgpool-II load balancing. It can also reattach nodes to EDB Pgpool-II when returned to the Failover Manager cluster. To configure Failover Manager for high availability using EDB Pgpool-II, you must set the following properties in the cluster properties file:
pgpool.enable = true pcp.user = User invoking PCP commands pcp.host = Virtual IP of EDB Pgpool-II or IP of NLB pcp.port = 9898 pcp.pass.file = Absolute path of PCPPASSFILE pgpool.bin = Absolute path of pgpool bin directory
Configuring EDB Pgpool-II
You can configure some important parameters in the
pgpool.conf file to integrate EDB Pgpool-II with Failover Manager.
Backend node setting
There are three PostgreSQL backend nodes: one primary and two standby
nodes. Configure using backend_* configuration parameters in
pgpool.conf, and use the equal backend weights for all nodes. This
makes the read queries distributed equally among all nodes.
backend_hostname0 = 'server1_IP'
backend_port0 = 5444
backend_weight0 = 1
backend_flag0 = 'ALLOW_TO_FAILOVER'
backend_hostname1 = 'server2_IP'
backend_port1 = 5444
backend_weight1 = 1
backend_flag1 = 'ALLOW_TO_FAILOVER'
backend_hostname2 = 'server3_IP'
backend_port2 = 5444
backend_weight2 = 1
backend_flag2 = 'ALLOW_TO_FAILOVER'Enabling load balancing and streaming replication mode
Set the following configuration parameter in the pgpool.conf file to enable load balancing and streaming replication mode:
For EDB Pgpool-II version 4.2:
backend_clustering_mode = 'streaming_replication' load_balance_mode = on
For EDB Pgpool-II versions prior to 4.2:
master_slave_mode = on master_slave_sub_mode = 'stream' load_balance_mode = on
Disabling health checking and failover
Health checking and failover are handled by Failover Manager, so disable them on the EDB Pgpool-II side. To disable the health check and failover on EDB Pgpool-II side, assign the following values:
health_check_period = 0
failover_on_backend_error = off
failover_if_affected_tuples_mismatch = off
failover_command = ''
failback_command = ''Ensure the following while setting up the values in the pgpool.conf file:
Keep the value of
wd_priorityinpgpool.confdifferent on each node. The node with the highest value gets the highest priority.The properties
backend_hostname0,backend_hostname1,backend_hostname2, and so on are shared properties (in Failover Manager terms) and must hold the same value in thepgpool.conffile on all the EDB Pgpool-II nodes.Update the correct interface value in
if_ *andarpingcmd props in thepgpool.conffile.Add the properties
heartbeat_destination0,heartbeat_destination1,heartbeat_destination2, and so on as per the number of nodes in thepgpool.conffile on every node. Here setheartbeat_destination0to the IP address or hostname of the local node.
Setting up PCP
The script uses the PCP interface, so you need to set up the PCP and
.PCPPASS file to allow PCP connections without a password prompt.
To set up PCP, see: Configuring pcp.conf.
To set up PCPPASS, see: PCP commands.
The load balancing is turned on to ensure read scalability by distributing read traffic across the standby nodes.
The health checking and error-triggered backend failover are turned off, as Failover Manager is responsible for performing health checks and triggering failover. We do not recommend using EDB Pgpool-II to perform health checking in this case, to avoid a conflict with Failover Manager or prematurely performing failover.
Finally, search_primary_node_timeout is set to a low value to
ensure prompt recovery of EDB Pgpool-II services upon a Failover
Manager-triggered failover.
Using virtual IP addresses
Both EDB Pgpool-II and Failover Manager provide the functionality to employ a virtual IP for seamless failover. While both provide this capability, the EDB Pgpool-II leader is the process that receives the application connections through the virtual IP. As in this design, such virtual IP management is performed by the EDB Pgpool-II watchdog system. Failover Manager VIP doesn't help in this design, so disable it.
In a failure situation of the active instance of EDB Pgpool-II (the primary EDB Pgpool-II server in our sample architecture), the next available standby EDB Pgpool-II instance (according to watchdog priority) is activated and takes charge as the leader EDB Pgpool-II instance.
Configuring the network load balancer
For Failover Manager / EDB Pgpool-II integration using the network load balancer in AWS or Azure, you need to perform some additional steps.
Add the following rules to the security groups to be used by the EDB Pgpool-II instances:
Rules for the security group to be used by the EDB Pgpool-II instances (SG Pgpool).
Type Protocol Port range Source Description Custom TCP TCP 9000 Entire Subnet Watchdog Custom TCP TCP 9694 Entire Subnet Heartbeat Custom TCP TCP 9898 Entire Subnet pcp Custom TCP TCP 9999 Entire Subnet Pgpool In addition to these rules, add the rules for SSH and Ping as per your requirement.
Rules for the security group to be used by the database instances (SG DB):
Type Protocol Port range Source Description Custom TCP TCP 7800 Entire Subnet Failover Manager Custom TCP TCP 5444 Entire Subnet Postgres
Setting these rules ensures that the ports required to run the database, Failover Manager, and EDB Pgpool-II are open for communication between the nodes and the load balancer for traffic routing and health monitoring.
In addition to these rules, add the rules for SSH and Ping as per your requirement.
Configuring NLB in Azure
If using AWS, see Configuring NLB in AWS.
After configuring the security group rules described in Configuring the network load balancer , follow the Azure documentation to:
Create a backend pool consisting of all the virtual machines running EDB Pgpool-II instances. Use the private IPs of the virtual machines to create the backend pool.
Add a health probe to check if the EDB Pgpool-II instance is available on the virtual machines. Set the protocol to
TCPand the port to9999.Add two load balancing rules, one each for port
9898and port9999. These rules ensure that the network traffic coming toward that port is distributed evenly among all the virtual machines present in the backend pool. Set the type toPublicload balancer orInternalload balancer.
After completing these configurations, you can connect to the database
on the IP address of the network load balancer on port 9999. If a
failure occurs on the primary database server, Failover Manager
promotes a new primary and then reconfigures EDB Pgpool-II to redistribute
traffic. If any of the EDB Pgpool-II processes is not available to accept
traffic, the network load balancer redistributes all the
traffic to the remaining two EDB Pgpool-II processes. Make sure that the
listen_backlog_multiplier parameter is tuned to compensate for the
higher number of connections in case of failover.
Configuring NLB in AWS
The following assumptions have been taken for the sample configuration:
All the EC2 instances and the load balancer are deployed in the same subnet. If required, you can add the database nodes to another subnet, but that requires a more complex configuration and might have a performance impact.
There is a security group for EDB Pgpool-II and a security group for the database instances.
After configuring the security group rules described in Configuring the network load balancer , follow the AWS documentation to:
Create two target groups with the following details:
Name Type Protocol Port VPC pcp Instances TCP 9898 Select the VPC to which the instances are connected. pgpool Instances TCP 9999 Select the VPC to which the instances are connected. Leave the rest of the settings (Health check TCP and Advanced health check settings) as default.
Register the created target groups with the instances that are running PgBouncer.
Create a load balancer with the following details:
Type VPC Listener PublicorInternal. EDB recommends using an internal load balancer.Choose a VPC and map it to the desired zones. Create a listener with TCPset to9898, and forward it to the target group pcp. Create another listener withTCPset to9999, and forward it to the target group pgpool.
After completing the configurations, you can connect to the database on
the IP address of the network load balancer on port 9999. If a failure
occurs on the primary database server, Failover Manager promotes a
new primary and then reconfigures EDB Pgpool-II to redistribute traffic. If any
of the EDB Pgpool-II processes is not available to accept traffic,
the network load balancer redistributes all the traffic to the
remaining two EDB Pgpool-II processes. Make sure that
listen_backlog_multiplier is tuned to compensate for the higher number
of connections in case of failover.