Quick start for Windows v15
EDB Postgres Advanced Server adds extended functionality to the open-source PostgreSQL database that supports database administration, enhanced SQL capabilities, database and application security, performance monitoring and analysis, and application development utilities. EDB Postgres Advanced Server also supports database compatibility features for Oracle users; for detailed information about compatibility features, see the EDB Postgres Advanced Server documentation.
This guide walks you through using the graphical installer to install EDB Postgres Advanced Server on a Windows system. The database created by this tutorial is well-suited for experimentation and testing. There are likely to be additional security and resource considerations when configuring a production installation that are not covered by this document.
This guide assumes that you are familiar with simple operating system and system administration procedures, and have administrative privileges on the host on which EDB Postgres Advanced Server is installed.
Components of an EDB Postgres Advanced Server deployment
Among the components that make up an EDB Postgres Advanced Server deployment are:
The database server - The database server (the postmaster) is the service that provides the key functionality that allows you to store and manage data. EDB Postgres Advanced Server is built on the PostgreSQL open-source database project; it includes all of the documented features of community PostgreSQL and more.
The database cluster - A cluster is a set of on-disk structures that comprise a collection of databases. A cluster is serviced by a single-instance of the database server. A database cluster is stored in the data directory. Don't store the data directory of a production database on an NFS file system.
Configuration files - You can use the parameters listed in Postgres configuration files to manage deployment preferences, security preferences, connection behaviors, and logging preferences.
Supporting tools, utilities, and clients - EDB makes available a full suite of tools and utilities that can help you monitor and manage your EDB Postgres Advanced Server deployment. For more information, visit the EDB website.
Supporting functions, procedures, data types, index types, operators, utilities, and aggregates - EDB Postgres Advanced Server includes a number of features that help you manage your data.
Installation prerequisites
User privileges
To perform an EDB Postgres Advanced Server installation on a Windows system, you must have administrator privileges. If you are installing EDB Postgres Advanced Server on a Windows system that is configured with User Account Control enabled, you can assume sufficient privileges to invoke the graphical installer by right clicking on the name of the installer and selecting Run as administrator from the context menu.
Windows-specific software requirements
You should apply Windows operating system updates before invoking the EDB Postgres Advanced Server installer. If (during the installation process) the installer encounters errors, exit the installation, and ensure that your version of Windows is up-to-date before restarting the installer.
Migration Toolkit or EDB*Plus installation Prerequisites
Before using StackBuilder Plus to install Migration Toolkit or EDB*Plus, you must first install Java (version 1.8 or later). If you are using Windows, Java installers and instructions are available online at:
http://www.java.com/en/download/manual.jsp
Installing and configuring EDB Postgres Advanced Server
The graphical installer provides a quick and easy way to install EDB Postgres Advanced Server 15 on a Windows system. Use the wizard's dialogs to specify information about your system and system usage; when you have completed the dialogs, the installer performs an installation based on the selections made during the setup process.
To invoke the wizard, you must have administrator privileges. Assume administrator privileges, and double-click the edb-as15-server-15.x.x-x-windows-x64 executable file.
Note
To install EDB Postgres Advanced Server on some versions of Windows, you may be required to right click on the file icon and select Run as Administrator from the context menu to invoke the installer with Administrator privileges.
When the Language Selection popup opens, select an installation language and click OK to continue to the Setup window.

Click Next to continue.
The EnterpriseDB License Agreement opens.
Carefully review the license agreement before highlighting the appropriate radio button; click Next to continue.
The Installation Directory window opens.
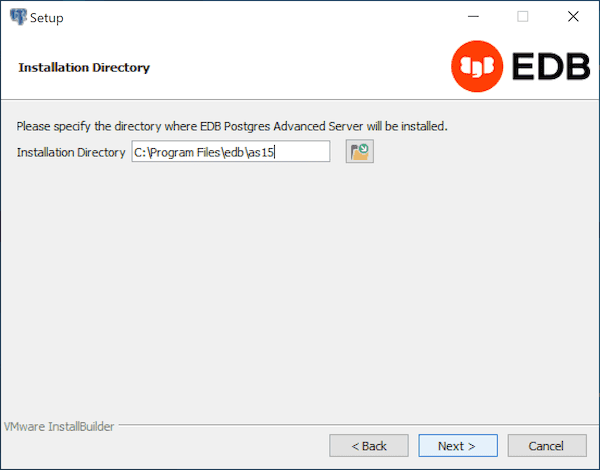
By default, the EDB Postgres Advanced Server installation directory is:
C:\Program Files\edb\as15
You can accept the default installation location, and click Next to continue, or optionally click the File Browser icon to open the Browse For Folder dialog to choose an alternate installation directory.
Note
The data directory of a production database should not be stored on an NFS file system.
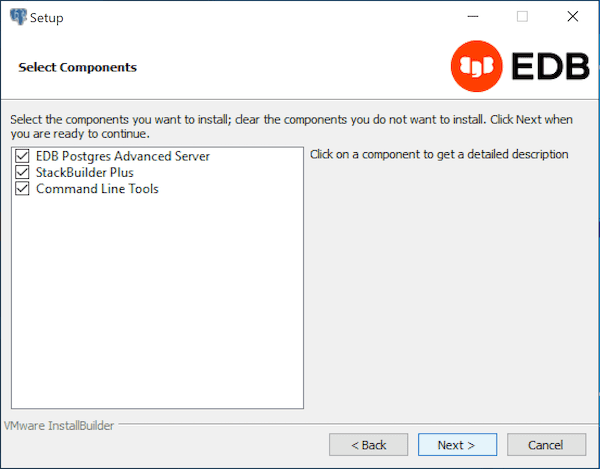
The Select Components window contains a list of optional components that you can install with the EDB Postgres Advanced Server Setup wizard. You can omit a module from the EDB Postgres Advanced Server installation by deselecting the box next to the components name.
The Setup wizard can install the following components while installing EDB Postgres Advanced Server 15:
EDB Postgres Advanced Server
Select the EDB Postgres Advanced Server option to install EDB Postgres Advanced Server 15.
StackBuilder Plus
The StackBuilder Plus utility is a graphical tool that can update installed products, or download and add supporting modules (and the resulting dependencies) after your EDB Postgres Advanced Server setup and installation completes.
Command Line Tools
The Command Line Tools option installs command line tools and supporting client libraries including:
- libpq
- psql
- EDB*Loader
- ecpgPlus
- pg_basebackup, pg_dump, and pg_restore
- pg_bench
- and more.
Note
The Command Line Tools are required if you are installing EDB Postgres Advanced Server or pgAdmin 4.
After selecting the components you wish to install, click Next to open the Additional Directories window.
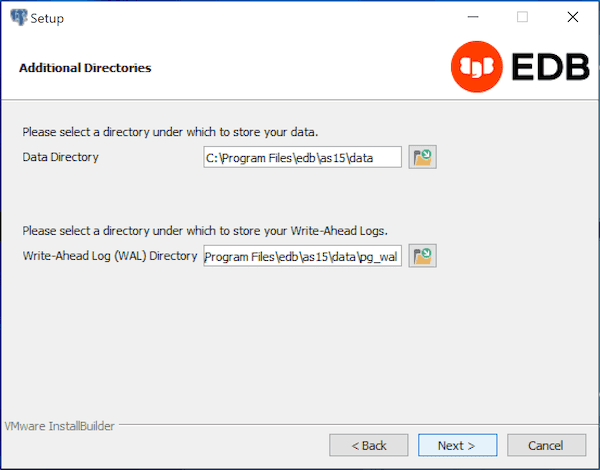
By default, the EDB Postgres Advanced Server data files are saved to:
C:\Program Files\edb\as15\data
The default location of the EDB Postgres Advanced Server Write-Ahead Log (WAL) Directory is:
C:\Program Files\edb\as15\data\pg_wal
EDB Postgres Advanced Server uses write-ahead logs to promote transaction safety and speed transaction processing; when you make a change to a table, the change is stored in shared memory and a record of the change is written to the write-ahead log. When you perform a COMMIT, EDB Postgres Advanced Server writes contents of the write-ahead log to disk.
Accept the default file locations, or use the File Browser icon to select an alternate location; click Next to continue to the EDB Postgres Advanced Server Dialect window.
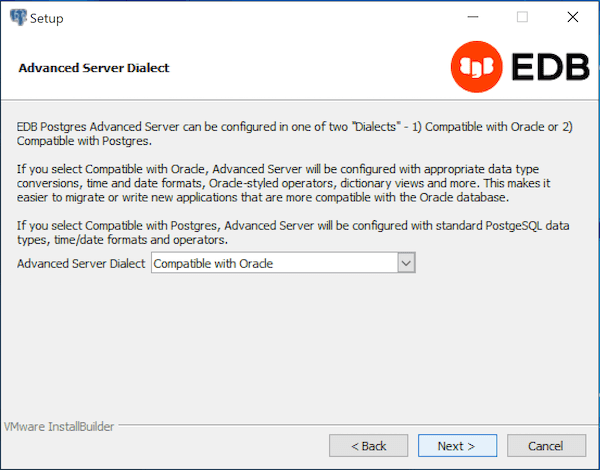
Use the drop-down listbox on the EDB Postgres Advanced Server Dialect window to choose a server dialect. The server dialect specifies the compatibility features supported by EDB Postgres Advanced Server.
By default, EDB Postgres Advanced Server installs in Compatible with Oracle mode; you can choose between Compatible with Oracle and Compatible with PostgreSQL installation modes.
Compatible with Oracle
If you select Compatible with Oracle, the installation includes the following features:
- Data dictionary views that is compatible with Oracle databases.
- Oracle data type conversions.
- Date values displayed in a format compatible with Oracle syntax.
- Support for Oracle-styled concatenation rules (if you concatenate a string value with a
NULLvalue, the returned value is the value of the string). - Schemas (
dboandsys) compatible with Oracle databases added to theSEARCH_PATH. - Support for the following Oracle built-in packages:
| Package | Functionality compatible with Oracle databases |
|---|---|
dbms_alert | Provides the capability to register for, send, and receive alerts. |
dbms_job | Provides the capability for the creation, scheduling, and managing of jobs. |
dbms_lob | Provides the capability to manage on large objects. |
dbms_output | Provides the capability to send messages to a message buffer, or get messages from the message buffer. |
dbms_pipe | Provides the capability to send messages through a pipe within or between sessions connected to the same database cluster. |
dbms_rls | Enables the implementation of Virtual Private Database on certain EDB Postgres Advanced Server database objects. |
dbms_sql | Provides an application interface to the EDB dynamic SQL functionality. |
dbms_utility | Provides various utility programs. |
dbms_aqadm | Provides supporting procedures for Advanced Queueing functionality. |
dbms_aq | Provides message queueing and processing for EDB Postgres Advanced Server. |
dbms_profiler | Collects and stores performance information about the PL/pgSQL and SPL statements that are executed during a performance profiling session. |
dbms_random | Provides a number of methods to generate random values. |
dbms_redact | Enables the redacting or masking of data that is returned by a query. |
dbms_lock | Provides support for the DBMS_LOCK.SLEEP procedure. |
dbms_scheduler | Provides a way to create and manage jobs, programs, and job schedules. |
dbms_crypto | Provides functions and procedures to encrypt or decrypt RAW, BLOB or CLOB data. You can also use DBMS_CRYPTO functions to generate cryptographically strong random values. |
dbms_mview | Provides a way to manage and refresh materialized views and their dependencies. |
dbms_session | Provides support for the DBMS_SESSION.SET_ROLE procedure. |
utl_encode | Provides a way to encode and decode data. |
utl_http | Provides a way to use the HTTP or HTTPS protocol to retrieve information found at an URL. |
utl_file | Provides the capability to read from, and write to files on the operating system’s file system. |
utl_smtp | Provides the capability to send e-mails over the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). |
utl_mail | Provides the capability to manage e-mail. |
utl_url | Provides a way to escape illegal and reserved characters within an URL. |
utl_raw | Provides a way to manipulate or retrieve the length of raw data types. |
This is not a comprehensive list of the compatibility features for Oracle included when EDB Postgres Advanced Server is installed in Compatible with Oracle mode. For more information, see Database compatibility for Oracle developers: built-in packages.
If you choose to install in Compatible with Oracle mode, the EDB Postgres Advanced Server superuser name is enterprisedb.
Compatible with PostgreSQL
If you select Compatible with PostgreSQL, EDB Postgres Advanced Server exhibits compatibility with PostgreSQL version 15. If you choose to install in Compatible with PostgreSQL mode, the default EDB Postgres Advanced Server superuser name is postgres.
For detailed information about PostgreSQL functionality, visit the official PostgreSQL website.
After specifying a configuration mode, click Next to continue to the Password window.
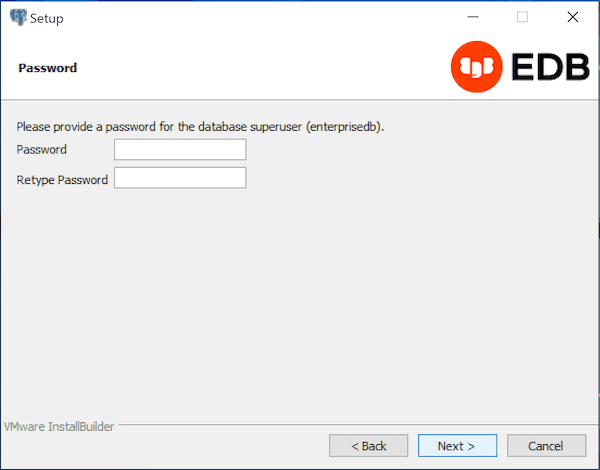
EDB Postgres Advanced Server uses the password specified on the Password window for the database superuser. The specified password must conform to any security policies existing on the EDB Postgres Advanced Server host.
After you enter a password in the Password field, confirm the password in the Retype Password field, and click Next to continue.
The Additional Configuration window opens.
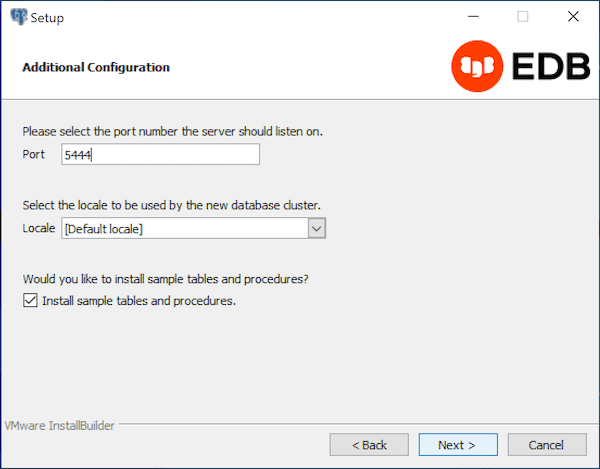
Use the fields on the Additional Configuration window to specify installation details:
- Use the
Portfield to specify the port number that EDB Postgres Advanced Server should listen to for connection requests from client applications. The default is5444. - If the
Localefield is set to[Default locale], EDB Postgres Advanced Server uses the system locale as the working locale. Use the drop-down listbox next toLocaleto specify an alternate locale for EDB Postgres Advanced Server. - By default, the
Setupwizard installs corresponding sample data for the server dialect specified by the compatibility mode(OracleorPostgreSQL). Clear the check box next toInstall sample tables and proceduresif you don't wish to have sample data installed.
After verifying the information on the Additional Configuration window, click Next to open the Dynatune Dynamic Tuning: Server Utilization window.
The graphical Setup wizard facilitates performance tuning via the Dynatune Dynamic Tuning feature. Dynatune functionality allows EDB Postgres Advanced Server to make optimal usage of the system resources available on the host machine on which it is installed.
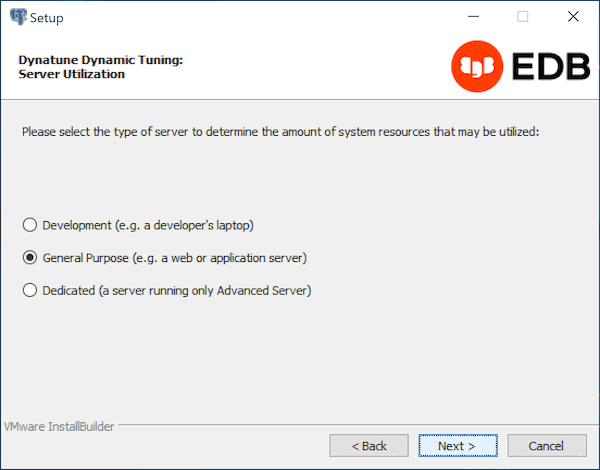
The edb_dynatune configuration parameter determines how EDB Postgres Advanced Server allocates system resources. Use the radio buttons on the Server Utilization window to set the initial value of the edb_dynatune configuration parameter:
- Select
Developmentto set the value ofedb_dynatuneto33. A low value dedicates the least amount of the host machine’s resources to the database server. This is a good choice for a development machine. - Select
General Purposeto set the value ofedb_dynatuneto66. A mid-range value dedicates a moderate amount of system resources to the database server. This would be a good setting for an application server with a fixed number of applications running on the same host as EDB Postgres Advanced Server. - Select
Dedicatedto set the value ofedb_dynatuneto100. A high value dedicates most of the system resources to the database server. This is a good choice for a dedicated server host.
After the installation is complete, you can adjust the value of edb_dynatune by editing the postgresql.conf file, located in the data directory of your EDB Postgres Advanced Server installation. After editing the postgresql.conf file, you must restart the server for your changes to take effect.
Select the appropriate setting for your system, and click Next to continue to the Dynatune Dynamic Tuning: Workload Profile window.
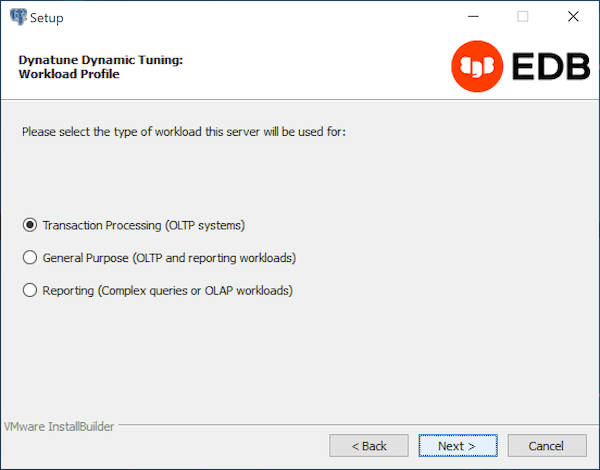
Use the radio buttons on the Workload Profile window to specify the initial value of the edb_dynatune_profile configuration parameter. The edb_dynatune_profile parameter controls performance-tuning aspects based on the type of work that the server performs.
- Select
Transaction Processing (OLTP systems)to specify anedb_dynatune_profilevalue ofoltp. Recommended when EDB Postgres Advanced Server is supporting heavy online transaction processing. - Select
General Purpose (OLTP and reporting workloads)to specify anedb_dynatune_profilevalue ofmixed. Recommended for servers that provide a mix of transaction processing and data reporting. - Select
Reporting (Complex queries or OLAP workloads)to specify anedb_dynatune_profilevalue ofreporting. Recommended for database servers used for heavy data reporting.
After the installation is complete, you can adjust the value of edb_dynatune_profile by editing the postgresql.conf file, located in the data directory of your EDB Postgres Advanced Server installation. After editing the postgresql.conf file, you must restart the server for your changes to take effect.
For more information about edb_dynatune and other performance-related topics, see the Dynatune.
By default, EDB Postgres Advanced Server is configured to start the service when the system boots. Click Next to continue.
The Pre Installation Summary opens.
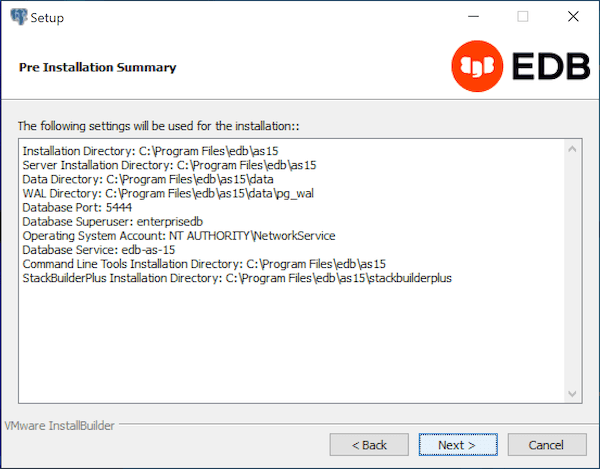
The Pre Installation Summary provides an overview of the options specified during the Setup process. Review the options before clicking Next; click Back to navigate back through the dialogs and update any options.
The Ready to Install window confirms that the installer has the information it needs about your configuration preferences to install EDB Postgres Advanced Server. Click Next to continue.
As each supporting module is unpacked and installed, the module’s installation is confirmed with a progress bar.
Before the Setup wizard completes the EDB Postgres Advanced Server installation, it offers to Launch StackBuilder Plus at exit?
You can clear the StackBuilder Plus check box and click Finish to complete the EDB Postgres Advanced Server installation, or accept the default and proceed to StackBuilder Plus.
EDB Postgres StackBuilder Plus is included with the installation of EDB Postgres Advanced Server and its core supporting components. StackBuilder Plus is a graphical tool that can update installed products, or download and add supporting modules (and the resulting dependencies) after your EDB Postgres Advanced Server setup and installation completes.
For more detailed product usage information, see the EDB Postgres Advanced Server documentation available at the EDB website.