Creating a Publication v6.2
Creating a publication requires the following steps:
- Registering the publication server
- Adding the primary definition node
- Creating a publication by choosing the tables for the publication along with the conflict resolution options
- Defining table filters to be enabled on any primary nodes
Registering a Publication Server
Registering a publication server is done in a manner identical to single-master replication. See Registering a Publication Server for directions on registering a publication server.
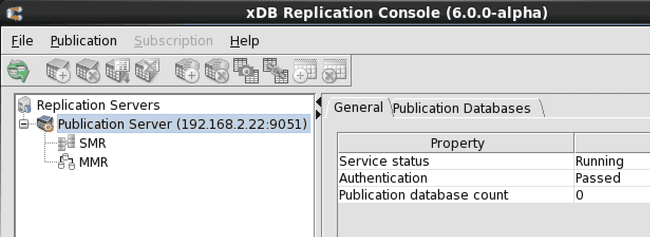
Figure 6-1: Replication tree after registering a publication server
After you have successfully registered a publication server, the replication tree of the xDB Replication Console displays a Publication Server node under which are the SMR and MMR type nodes.
Continue to build the multi-master replication system under the MMR type node.
Adding the Primary definition node
The first database to be identified to xDB Replication Server is the primary definition node. This is done by creating a publication database definition subordinate to the MMR type node under the Publication Server node.
After the publication database definition is created, a Publication Database node representing the primary definition node appears in the replication tree of the xDB Replication Console. A publication containing tables residing within this database can then be created under the Publication Database node.
You must enter database connection information such as the database server network address, database identifier, and database login user name and password when you create the publication database definition. The connection information is used by the publication server to access the publication tables when it performs replication.
Step 1: Make sure the database server for the primary definition node is running and accepting client connections.
Step 2: Select the MMR type node under the Publication Server node. From the Publication menu, choose Publication Database, and then choose Add Database. Alternatively, click the secondary mouse button on the MMR type node and choose Add Database. The Publication Service – Add Database dialog box appears.
Step 3: Fill in the following fields:
Database Type. Select PostgreSQL or Postgres Plus Advanced Server for the primary definition node. For an Advanced Server Oracle compatible installation, select the Postgres Plus Advanced Server option. For PostgreSQL or an Advanced Server PostgreSQL compatible installation, select the PostgreSQL option.Host. IP address of the host on which the primary definition node is running.Port. Port on which the primary definition node is listening for connections.User. The database user name for the primary definition node created in Step 1 of Preparing the Primary definition node.Password. Password of the database user.Database. Enter the database name of the primary definition node.URL Options (For SSL connectivity). Enter the URL options to establish SSL connectivity to the primary definition node. See Using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Connections for information on using SSL connections.Changeset Logging (For Postgres). Select Table Triggers to use the trigger-based method of synchronization replication. Select WAL Stream to use the log-based method of synchronization replication. See Synchronization Replication with the Trigger-Based Method for information on the trigger-based method. See Synchronization Replication with the Log-Based Method for information on the log-based method.Node Priority Level. An integer from 1 to 10, which is the priority level assigned to this primary node for conflict resolution based on node priority. The highest priority is 1 while the lowest is 10. See Conflict Resolution Strategies for information on conflict resolution strategies. The default is 1 for the primary definition node.
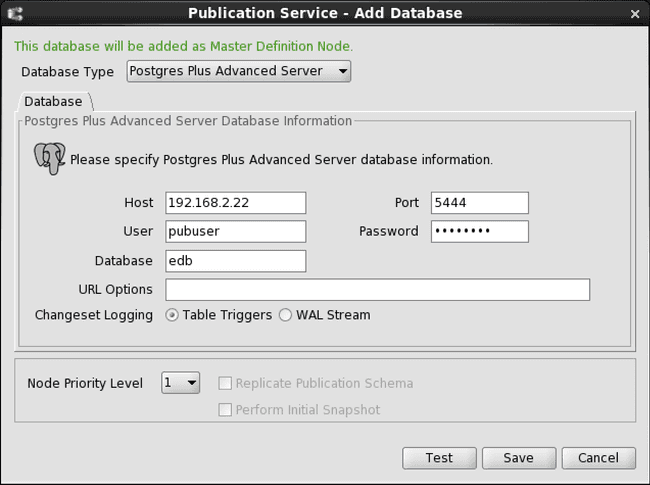
Figure 6-2: Publication Service - Add Database dialog box for the primary definition node
Step 4: Click the Test button. If Test Result: Success appears, click the OK button, then click the Save button.
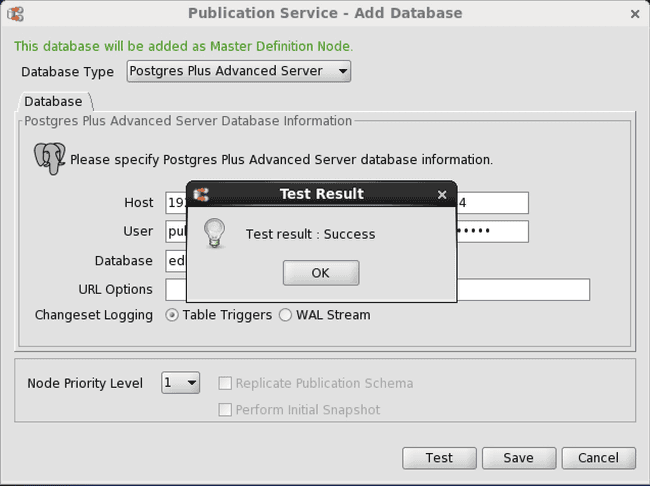
Figure 6-3: Successful primary definition node test
If an error message appears investigate the cause of the error, correct the problem, and repeat steps 1 through 4.
When the publication database definition is successfully saved, a Publication Database node is added to the replication tree under the MMR type node of the Publication Server node.
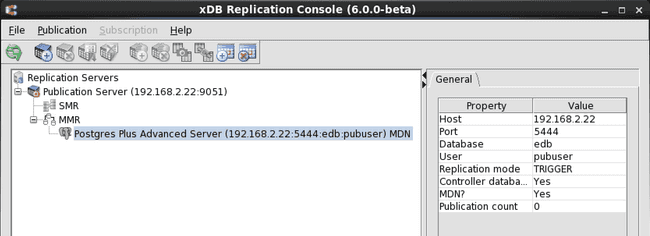
Figure 6-4: Replication tree after adding the primary definition node
The label MDN appears at the end of the node in the replication tree and in addition, the MDN field is set to Yes in the Property window to indicate this is the primary definition node.
Adding a Publication
Subordinate to the primary definition node, you create a publication that contains tables of the database.
Step 1: Select the Publication Database node. From the Publication menu, choose Create Publication. Alternatively, click the secondary mouse button on the Publication Database node and choose Create Publication. The Create Publication dialog box appears.
Step 2: Fill in the following fields under the Create Publication tab:
Publication Name. Enter a name that is unique amongst all publications.Publish. Check the boxes next to the tables that are to be included in the publication. Alternatively or in addition, click theUse Wildcard Selectionbutton to use wildcard pattern matching for selecting publication tables.Select All. Check this box if you want to include all tables in the Available Tables list in the publication.Use Wildcard Selection. Click this button to use the wildcard selector to choose tables for the publication. See Selecting Tables with the Wildcard Selector for information on the wildcard selector.
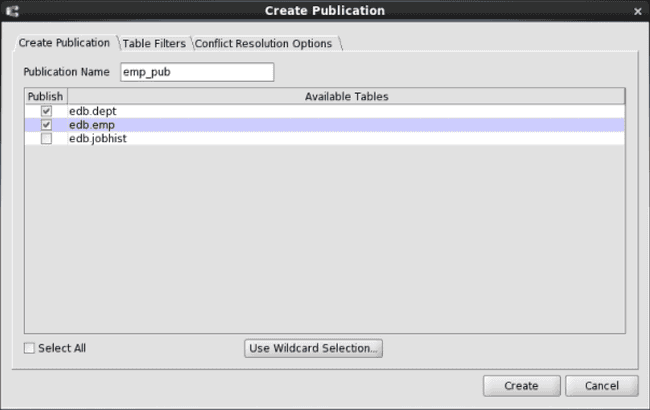
Figure 6-5: Create Publication dialog box
If you wish to use table filters during replications between primary nodes in this multi-master replication system, follow the directions in the next step to define the initial set of available table filters, otherwise go on to Step 4.
Step 3 (Optional): Table filters consist of a set of filter rules that control the selection criteria for rows replicated between primary nodes during a snapshot or a synchronization replication.
Note
See Table Settings and Restrictions for Table Filters for table setup requirements for a log-based replication system as well as general restrictions on the use of table filters.
A filter rule consists of a filter name and a SQL WHERE clause (omitting the WHERE keyword) called the filter clause, which you specify for a table that defines the selection criteria for rows that are to be included during a replication.
Multiple filter rules may be defined for each table in the publication. If no filter rule is defined for a given table, then no filtering can be later enabled on that corresponding table in any primary node of the multi-master replication system.
After filter rules have been defined for a publication table, you can later choose whether or not to enable those filter rules on any primary node in the replication system in accordance with the following rules.
- At most one filter rule can be enabled on a given table in a given primary node.
- The same filter rule may be enabled on the same given table in several, different primary nodes.
- Different filter rules may be enabled on the same given table but in different primary nodes.
If you want to define table filters on the publication tables, click the Table Filters tab. Select the table from the Table/View drop-down list for which you wish to add a filter rule. Click the Add Filter button.
In the Filter dialog box, enter a descriptive filter name and the filter clause to select the rows you want to replicate. The filter name and filter clause must meet the following conditions:
- For any given table, each filter rule must be assigned a unique filter name.
- For any given table, the filter clauses must have different syntaxes (that is, the filtering criteria must be different).
In the following example a filter rule is defined on the dept table so only rows where the deptno column contains 10, 20, or 30 are included in replications. All other rows are excluded from replication.
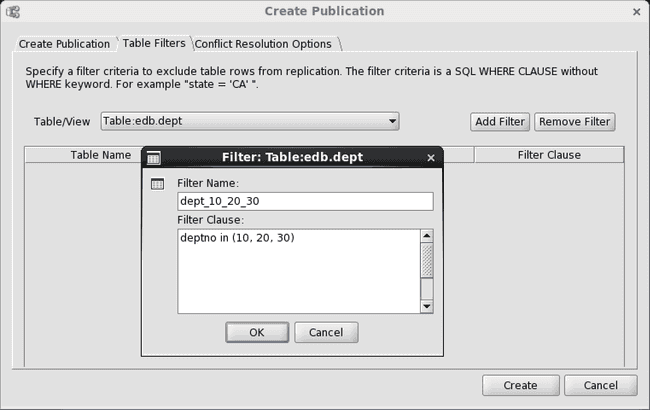
Figure 6-6: Adding a filter rule for the dept table
The following shows a rule added to the emp table by choosing edb.emp from the Table/View drop-down list and then entering the selection criteria for only rows with deptno containing 10 in the Filter dialog box.
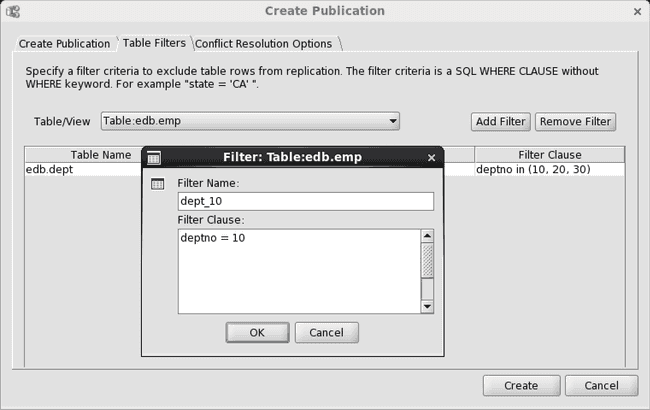
Figure 6-7: Adding a filter rule for the emp table
Repeating this process, additional filter rules can be added for the emp table. The following shows the complete set of available filter rules defined for the dept and emp tables.
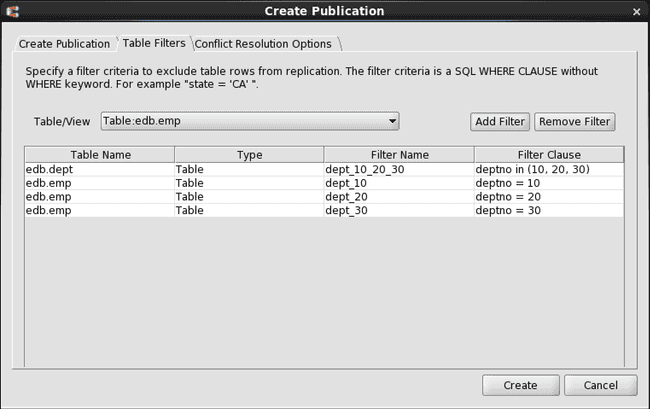
Figure 6-8: Set of all available filter rules
To remove a filter rule, click the primary mouse button on the filter rule you wish to remove so the entry is highlighted and then click the Remove Filter button.
You may also modify the filter name or filter clause of a filter rule listed in the Table Filters tab by double-clicking on the cell of the filter name or filter clause you wish to change. When the cursor appears in the cell, enter the text for the desired change.
When creating additional primary nodes, you may selectively enable these table filters on the corresponding tables in the additional primary nodes. See Creating Additional Primary nodes for information on creating additional primary nodes.
Note
To enable table filters on the primary definition node under which you are currently creating the publication, you must first switch the role of the primary definition node to a different primary node (see Switching the Primary definition node), and then follow the directions in Section Enabling/Disabling Table Filters on a Primary node to enable the table filters.
This completes the process of defining table filters. The next step is changing conflict resolution options.
If you wish to change the conflict resolution options from their default settings, follow the directions in the next step, otherwise go on to Step 5.
Step 4 (Optional): If you want to modify or see the current conflict resolution options, click the Conflict Resolution Options tab. For each table, you can select the primary conflict resolution strategy and a standby strategy by clicking the primary mouse button over the appropriate box to expose a drop-down list of choices.
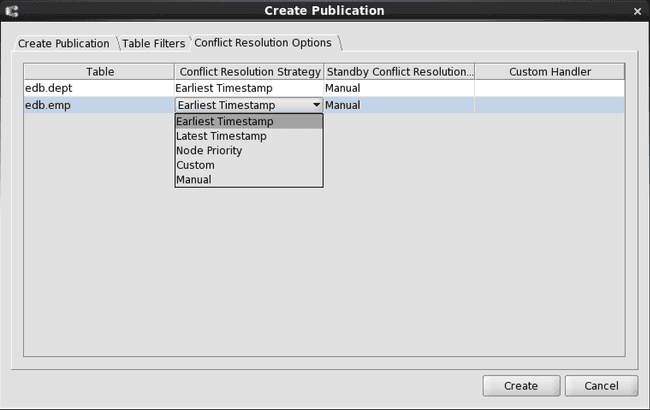
Figure 6-9: Conflict Resolution Options tab
If during synchronization replication, conflicting changes are pending against the same row from different primary nodes, the conflict resolution strategy determines which of the conflicting changes is accepted and replicated to all primary nodes. The conflicting changes that are not accepted are discarded.
If the selection from the Conflict Resolution Strategy column does not resolve the conflict, the selection from the Standby Conflict Resolution Strategy column is applied. If neither strategy resolves the conflict, the event is marked as Pending in the Conflict History tab. See Viewing Conflict History for information on viewing conflict history.
An example of a conflict is when the same column of the same row is changed by transactions in two different primary nodes. Depending upon the conflict resolution strategy in effect for the table, one of the transactions is accepted and replicated to all primary nodes. The other transaction is discarded and not replicated to any primary node.
The following is a brief summary of each conflict resolution strategy:
Earliest Timestamp. The conflicting change with the earliest timestamp is accepted and replicated to all other primary nodes. All other conflicting changes are discarded.Latest Timestamp. The conflicting change with the latest timestamp is accepted and replicated to all other primary nodes. All other conflicting changes are discarded.Node Priority. The conflicting change occurring on the primary node with the highest priority level is accepted and replicated to all other primary nodes. All other conflicting changes are discarded.Custom. Update/update conflicts are resolved with a PL/pgSQL custom conflict handling program.Manual. The conflict remains unresolved. Conflicting changes remain applied in each primary node where they originated, but are not replicated to other primary nodes. The proper adjustments must be manually applied in each primary node.
See Conflict Resolution Strategies for more information on conflict resolution strategies.
Step 5: If you expect update/update conflicts, then set the REPLICA IDENTITY option to FULL on those tables where the conflicts are expected to occur. See Configuration Parameter and Table Setting Requirements for additional information.
Step 6: Click the Create button. If Publication Created Successfully appears, click the OK button, otherwise investigate the error and make the necessary corrections.
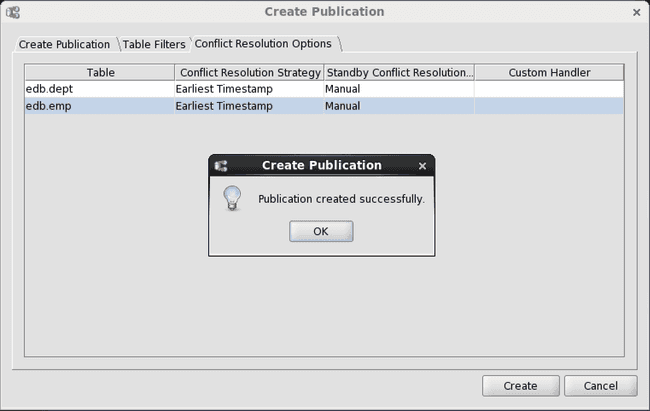
Figure 6-10: Publication created successfully
Upon successful publication creation, a Publication node is added to the replication tree.
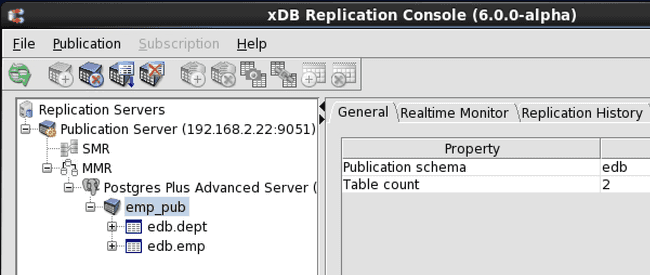
Figure 6-11: Replication tree after adding a publication