On Demand Replication v6.2
After a primary definition node, its publication, and additional primary nodes are created, there are a couple of choices for starting the replication process.
- Replication can be done immediately by performing an initial on demand snapshot after which synchronization replication may be performed.
- Replication can be scheduled to start at a later date and time by creating a schedule.
This section discusses the procedure for initiating a replication on demand. Section Creating a Schedule discusses how to create a schedule.
Performing Snapshot Replication
A snapshot replication occurs from the primary definition node to a selected primary node.
When you create a primary node for the first time, you have the option of performing an initial snapshot (see Step 3 of Creating Additional Primary nodes). You can perform snapshots to this primary node at any later point in time according to the following steps.
Step 1: Select the Publication node under the primary node for which you wish to perform snapshot replication.
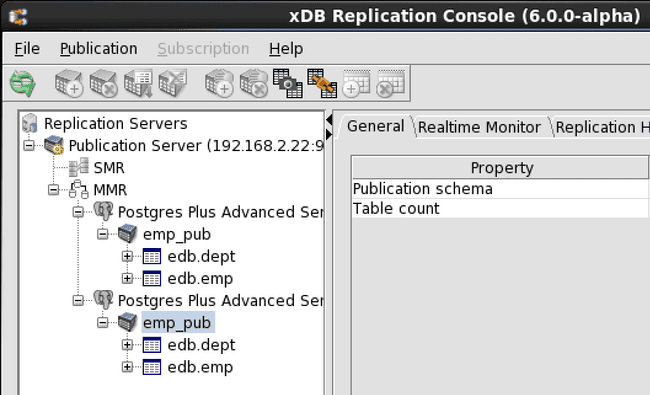
Figure 6-19: Selecting a primary node publication for an on demand snapshot
Step 2: Open the Snapshot dialog box in any of the following ways:
- Click the secondary mouse button on the Publication node and choose Snapshot.
- Click the primary mouse button on the Snapshot icon.
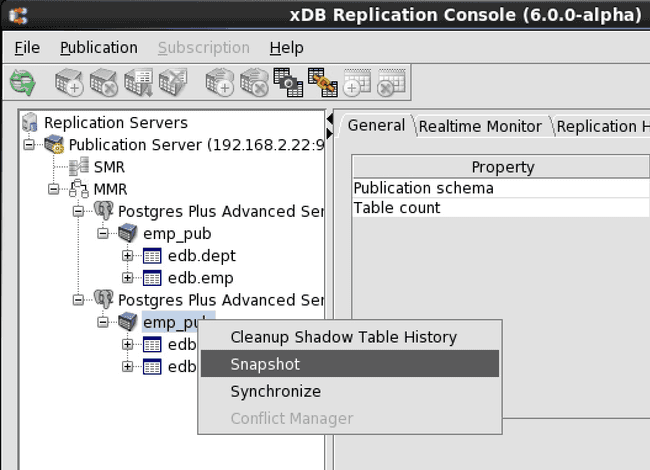
**Figure 6-20: Opening the Snapshot dialog box
Step 3: Select the Verbose Output check box only if you want to display the output from the snapshot in the dialog box. This option should be left unchecked in a network address translation (NAT) environment as a large amount of output from the snapshot may delay the response from the Snapshot dialog box. Click the Snapshot button to start snapshot replication.
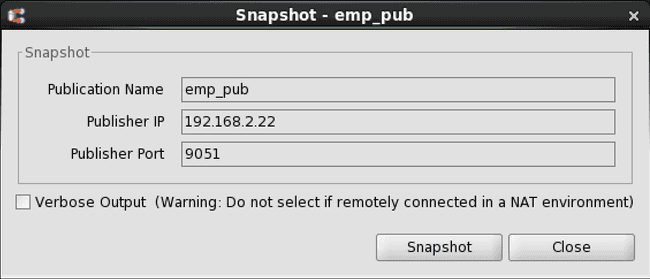
Figure 6-21: Snapshot dialog box
Step 4: Snapshot Taken Successfully appears if the snapshot was successful. Click the OK button. If the snapshot was not successful, scroll through the messages in the Snapshot dialog box window if Verbose Output was selected or check the log files.
The status messages of each snapshot are saved in the Migration Toolkit log files named mtk.log[.n] (where [.n] is an optional history file count if log file rotation is enabled) in the following directories:
For Linux:
/var/log/xdb-x.x
For Windows:
POSTGRES_HOME\.enterprisedb\xdb\x.x
POSTGRES_HOME is the home directory of the Windows postgres account (enterprisedb account for Advanced Server installed in Oracle compatible configuration mode). The specific location of POSTGRES_HOME is dependent upon your version of Windows. The xDB Replication Server version number is represented by x.x.
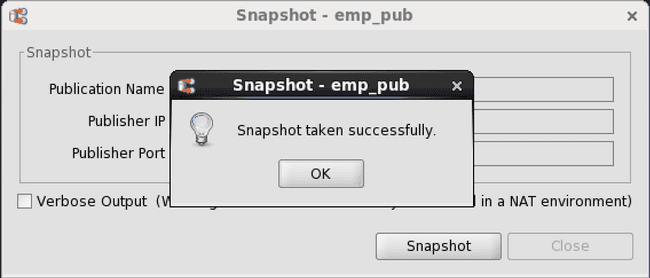
Figure 6-22: Successful on demand snapshot
The publication has now been replicated from the primary definition node to the selected primary node. A record of the snapshot is maintained in the replication history. See Viewing Replication History for information on how to view replication history.
Performing Synchronization Replication
Note
Be sure an initial snapshot replication has been performed from the primary definition node to every other primary node in the multi-master replication system. If a newly added primary node did not undergo an initial snapshot, any subsequent synchronization replication may fail to apply the transactions to that primary node. The initial snapshot could be taken when the primary node is first added (see Creating Additional Primary nodes) or by performing an on demand snapshot (see Performing Snapshot Replication).
When synchronization replication is performed in a multi-master replication system, a series of synchronization operations occur between every primary node pair in the replication system.
For example, if a replication system consists of primary nodes A, B, and C, synchronization is applied to the following node pairs whenever synchronization replication is initiated:
- Changes on node A are applied to node B.
- Changes on node A are applied to node C.
- Changes on node B are applied to node A.
- Changes on node B are applied to node C.
- Changes on node C are applied to node A.
- Changes on node C are applied to node B.
There may be circumstances where changes made on different nodes result in conflicts. Section Conflict Resolution discusses the types of conflicts that may occur and how they can be resolved.
The following steps describe how to initiate on demand synchronization replication.
Step 1: Select the Publication node under any primary node. Regardless of the primary node chosen, synchronization is applied to every primary node pair in the replication system.

Figure 6-23: Selecting a primary node publication for an on demand synchronization
Step 2: Open the Synchronize dialog box in any of the following ways:
- Click the secondary mouse button on the Publication node and choose
Synchronize. - Click the primary mouse button on the Synchronize icon.
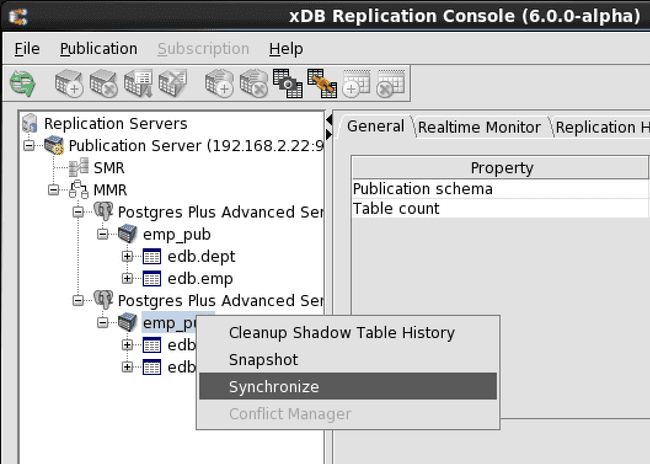
Figure 6-24: Opening the Synchronize dialog box
Step 3: Click the Synchronize button to start synchronization replication.
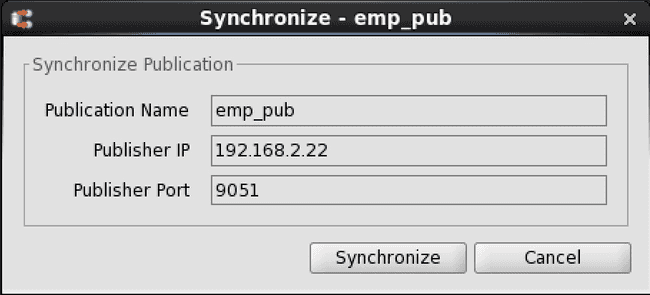
Figure 6-25: Synchronize dialog box
Step 4: Publication Synchronized Successfully(()) appears if the synchronization was successful. Click the OK button. If the synchronization was not successful, an error message is displayed.
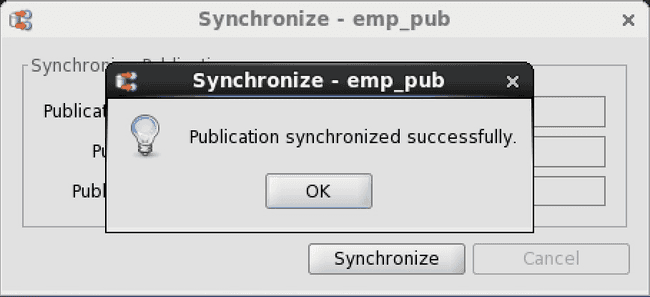
Figure 6-26: Successful on demand synchronization
The operations that were applied to the publication tables can be seen in the replication history. See Viewing Replication History for information on how to view replication history.
Conflicting changes that were encountered can be seen in the conflict history. See Viewing Conflict History for information on how to view conflict history.