Distributed replication v7
Replication Server provides the flexibility for you to run the replication system’s components on separate machines on a network.
Replication Server is designed so that you can set up replication systems where:
- Each of the components (publication server, subscription server, publication database, subscription database, and primary nodes) can all run on the same host
- Each component can run on its own separate host
- Any combination of components can run on any number of hosts
However, for practical purposes, there are two basic scenarios. The simplest case is where all components are on the same host. The other case is where you have the Oracle or SQL Server database server running on a host separate from the rest of the replication system components.
Each scenario has advantages and disadvantages.
Single host
The simplest implementation of a replication system is when all replication components run on a single host. This means that the PostgreSQL or EDB Postgres Advanced Server installation, the complete Replication Server installation (publication server and subscription server), and the Oracle or SQL Server database server reside on the same machine.
The Postgres publication or subscription database can reside in the initial database cluster created when Postgres is installed on the host.
The advantages of a single-host replication system are the following:
- Performance is better since there's no network over which to push replication data, especially if large snapshots are involved.
- Configuration is much simpler. When creating the replication system logical components, the IP addresses of all components are the same.
The disadvantages of a single host replication system are the following:
- The replication system and the database servers all consume the resources of one machine, which can adversely affect database application performance.
- The publication and subscription databases might be in different geographic locations, thereby requiring multiple networked hosts.
- Your site might require the use of a dedicated host for the Oracle or SQL Server database server, so Replication Server can't reside on the same machine.
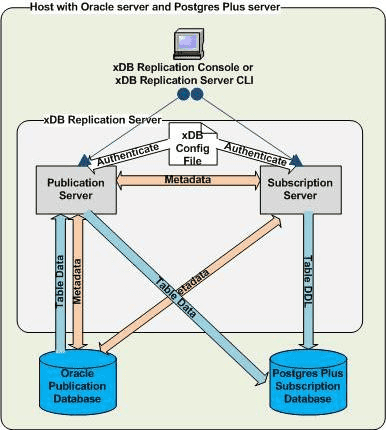
Single-master replication distributed hosts
Replication Server allows you to build a replication system with either or both of the publication database and the subscription database on separate hosts, as shown in the figure:
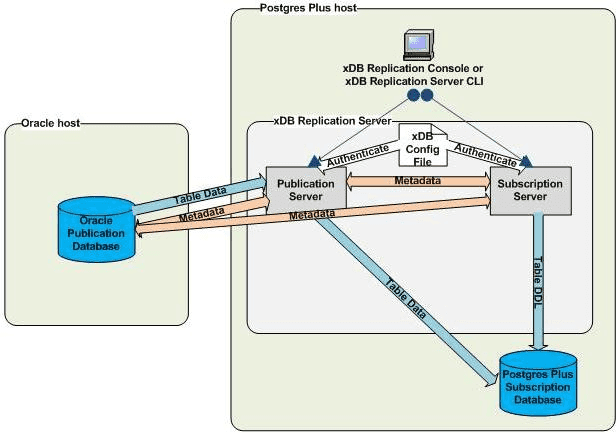
You can use the same remote distribution for the subscription database instead of or in addition to the publication database.
The advantages of a distributed host replication system are the following:
- The replication system and the database servers can each consume the resources of their own machines, which you can individually select and tune.
- The publication and subscription databases can be in different geographic locations.
- You can enforce stronger database security if only the database server is allowed to run on a host.
The disadvantages of a distributed host replication system are the following:
- There might be a performance disadvantage since there is a network over which to push replication data, especially if large snapshots are involved.
- Installation is more complex if the Postgres database must run on a different host than Replication Server. Installation involves installing Postgres on two separate hosts.
- Configuration is more complex. The network and firewalls must be properly configured to allow the distributed components to communicate. When creating the replication system logical components, you must use the correct IP addresses of all components. In addition, you must keep the correct IP addresses up to date in the replication system control schema if they change in the networked environment.
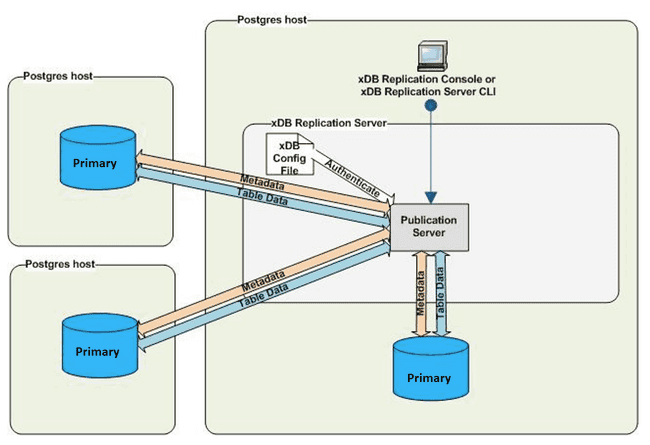
Multi-master replication distributed hosts
In a multi-master replication system, the Postgres database servers running the primary nodes can run on a single or multiple hosts. The following figure shows two primary nodes running on database servers on separate hosts as well as a primary node running on the same database server as the publication server.