Installing and configuring the .NET Connector v6.0.2.1
Installing the .NET Connector
You can use the EDB .NET Connector Installer (available from the EDB website) to add the .NET Connector to your system. After downloading the installer, right-click on the installer icon, and select Run As Administrator from the context menu. When prompted, select an installation language and click OK to continue to the Setup window.

Click Next to continue.
Use the Installation Directory dialog to specify the directory in which the connector will be installed, and click Next to continue.
Click Next on the Ready to Install dialog to start the installation; popup dialogs confirm the progress of the installation wizard.
When the wizard informs you that it has completed the setup, click the Finish button to exit the dialog.
You can also use StackBuilder Plus to add or update the connector on an existing Advanced Server installation; to open StackBuilder Plus, select StackBuilder Plus from the Windows Apps menu.
When StackBuilder Plus opens, follow the onscreen instructions.
Select the EnterpriseDB.Net Connector option from the Database Drivers node of the tree control.
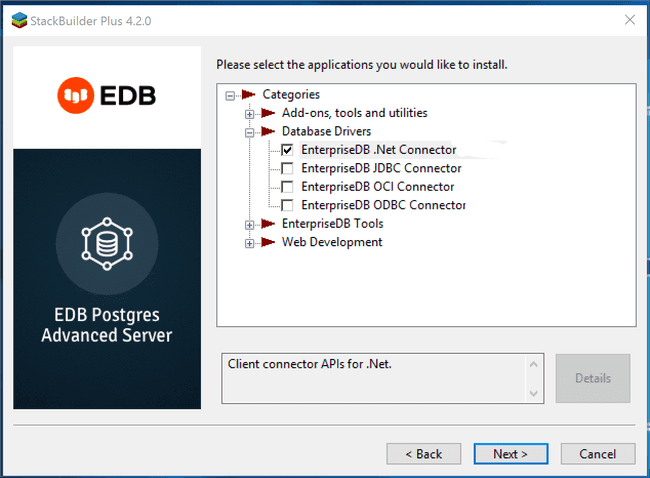
Follow the directions of the onscreen wizard to add or update an installation of an EDB Connector.
Configuring the .NET Connector
Please see the following environment-specific sections for information about configuring the .NET Connector:
- Referencing the Library Files. General configuration information applicable to all components.
- .NET 6.0 Instructions for configuring for use with .NET 6.0.
- .NET 5.0 Instructions for configuring for use with .NET 5.0.
- .NET Core 3.1 Instructions for configuring for use with .NET Core 3.1.
- .NET Standard 2.0 Instructions for configuring for use with .NET Standard 2.0.
- .NET Standard 2.1 Instructions for configuring for use with .NET Standard 2.1.
- .NET EntityFramework Core Instructions for configuring for use with .NET EntityFramework Core.
Referencing the library files
To reference library files with Microsoft Visual Studio:
- Select the project in the
Solution Explorer. - Select
Add Referencefrom theProjectmenu. - When the
Add Referencedialog box opens, browse to select the appropriate library files.
Optionally, the library files can be copied to the specified location.
Before you can use an EDB .NET class, you must import the namespace into your program. Importing a namespace makes the compiler aware of the classes available within the namespace. The namespace is:
EnterpriseDB.EDBClient
The method you use to include the namespace varies by the type of application you are writing. For example, the following command imports a namespace into an ASP.NET page:
<% import namespace="EnterpriseDB.EDBClient" %>
To import a namespace into a C# application, write:
using EnterpriseDB.EDBClient;
.NET framework setup
The following sections describe the setup for various .NET versions.
.NET 6.0
For .NET 6.0, the data provider installation path is:
C:\Program Files\edb\dotnet\net6.0\
You must add the following dependencies to your project:
EnterpriseDB.EDBClient.dll
Depending upon the type of application you use, you may be required to import the namespace into the source code. See Referencing the Library Files for this and other information about referencing library files.
.NET 5.0
For .NET 5.0, the data provider installation path is:
C:\Program Files\edb\dotnet\net5.0\
You must add the following dependencies to your project:
EnterpriseDB.EDBClient.dll
Depending upon the type of application you use, you may be required to import the namespace into the source code. See Referencing the Library Files for this and other information about referencing library files.
.NET Core 3.1
If you are using .NET Core 3.1, the data provider installation path is:
C:\Program Files\edb\dotnet\netcoreapp3.1\
The following shared library files are required:
EnterpriseDB.EDBClient.dll
System.Threading.Tasks.Extensions.dll
System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe.dll
System.ValueTuple.dll
System.Memory.dll
Depending upon the type of application you use, you may be required to import the namespace into the source code. See Referencing the Library Files for this and other information about referencing library files.
.NET Standard 2.0
For .NET Standard Framework 2.0, the data provider installation path is:
C:\Program Files\edb\dotnet\netstandard2.0\
You must add the following dependencies to your project:
EnterpriseDB.EDBClient.dll
System.Threading.Tasks.Extensions.dll
System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe.dll
System.ValueTuple.dll
Note
If your target framework is .Net Core 2.0, then include the following file in your project:
System.Threading.Tasks.Extensions.dll
Depending upon the type of application you use, you may be required to import the namespace into the source code. See Referencing the Library Files for this and other information about referencing library files.
.NET Standard 2.1
For .NET Standard Framework 2.1, the data provider installation path is:
C:\Program Files\edb\dotnet\netstandard2.1\
The following shared library files are required:
EnterpriseDB.EDBClient.dll
System.Memory.dll
System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe.dll
System.Text.Json.dll
System.Threading.Tasks.Extensions.dll
System.ValueTuple.dll
Depending upon the type of application you use, you may be required to import the namespace into the source code. See Referencing the Library Files for this and other information about referencing library files.
.NET EntityFramework Core
To configure the .NET Connector for use with Entity Framework Core, the data provider installation path is:
C:\Program Files\edb\dotnet\EFCore
The following shared library file is required:
EnterpriseDB.EDBClient.EntityFrameworkCore.PostgreSQL.dll
Note
Entity Framework Core can be used with the EnterpriseDB.EDBClient.dll library available in the net6.0 subdirectory.
See Referencing the Library Files for information about referencing library files.
The following NuGet packages are required:
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Relational
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Abstractions
For usage information about Entity Framework Core, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
Prerequisite:
Install dotnet-ef (using Command Prompt)
dotnet tool install --global dotnet-ef
Sample project
Create a new Console Application based on .NET 6.0.
Add Reference to the following EDB assemblies:
EnterpriseDB.EDBClient.EntityFrameworkCore.PostgreSQL.dll
EnterpriseDB.EDBClient.dll
Add the following NuGet packages:
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Relational
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Abstractions
Command Prompt
Open Tools → Command Line → Developer Command Prompt
Database first scenario
Issue the following command to create Model Classes corresponding to all objects in the specified database:
dotnet ef dbcontext scaffold Host=<HOST>;Database=<DATABASE>;Username=<USER>;Password=<PASSWORD>;Port=<PORT> EnterpriseDB.EDBClient.EntityFrameworkCore.PostgreSQL -o Models
Code first scenario
Add code for defining a DbContext and create, read, update & delete operations.
Please refer to the Microsoft documentation for further details.
Issue the following commands to create the initial database and tables:
dotnet ef migrations add InitialCreate --context BloggingContext
dotnet ef database update --context BloggingContext