Monitoring Barman v9
Barman (Backup and Recovery Manager) is an open-source administration tool for remote backups and disaster recovery of PostgreSQL servers in business-critical environments. It relies on PostgreSQL’s point-in-time recovery technology, allowing DBAs to remotely manage a complete catalog of backups and the recovery phase of multiple remote servers from one location. For more information, see Barman.
Starting with version 8.4, you can monitor a Barman server through the PEM console.
Prerequisites for monitoring Barman
Before adding a Barman server to the PEM console:
- You must manually install and configure Barman on the Barman host. For more information about installing and configuring Barman, see Barman.
- Install the pg-backup-api tool on Barman host. For more information about installing, see pg-backup-api.
Configuring a Barman server
You can configure and edit your Barman server using:
- PEM web client
pemworkercommand line
Using PEM web client
Configure
You can use the Create–BARMAN Server dialog box to register an existing Barman server with the PEM server. To open the dialog box, right-click the BARMAN Servers node and select Create-BARMAN Server.
Use the General tab to describe the general properties of the Barman server:
Use the Name field to specify a name for the server. The name identifies the server in the browser tree.
Use the URL field to specify the URL of the host where Barman is installed.
Use the Team field to specify a PostgreSQL role name. Only PEM users who are members of this role, who created the server initially, or have superuser privileges on the PEM server can see this server when they log on to PEM. If this field is left blank, all PEM users see the server.
Use the PEM Agent tab to specify connection details for the PEM Agent:
Use the Bound Agent field to select the agent that you want to configure as a Barman server. Only those PEM agents that are supported for Barman are listed.
Use the Probe Frequency field to specify the number of seconds to execute the probes with the specified interval.
Use the Hearbeat field to specify the interval to check the availability of PEM agent in seconds.
Note
After registering the Barman server, you need to restart the PEM agent.
Editing
To edit your Barman server, right-click the server from the browser tree and select Properties.
Use the PEM Agent tab to modify the bound agent, probe frequency, and heartbeat. Only the owner of the Barman server can modify the fields on the PEM Agent tab.
Use the Information tab to view the detailed information about your Barman server. This tab gets populated whenever the Barman related probes are executed.
Use the Configuration tab to view the configuration settings of your Barman server. This tab gets populated whenever the Barman related probes are executed.
Using pemworker command line
You can configure Barman server using pemworker command line options.
asheshvashi@pem:~/PEM/agent$ ./pemworker --update-barman --help
./pemworker --update-barman [barman-update-options]
barman-update-options:
--id <barman-id> (ID for the existing BARMAN API 'pg-backup-api')
--api-url <url> (URL of the BARMAN API 'pg-backup-api')
--probe-execution-frequency <interval> (Default: 30, Probe the BARMAN API 'pg-backup-api' at regular interval 'in seconds' and fetch the metrics.)
--heartbeat-interval <interval> (Default: 10, Ping the BARMAN API 'pg-backup-api' 'status' API at a regular interval 'in seconds' for checking its availability.)
--ssl-crt <certificate_file> (SSL certificate file for the BARMAN API.)
--ssl-key <key_file> (Private SSL key for the BARMAN API.)
--ssl-ca-cert <ca_file> (CA certificate to verify peer against the BARMAN API.)
--config-file/-c <config_file> (Path to the agent configuration file.)
asheshvashi@pem:~/PEM/agent$ ./pemworker --unregister-barman --help
./pemworker --unregister-barman [barman-unregistration-options]
barman-unregistration-options:
--id <barman-id> (ID for the existing BARMAN API, registered with the PEM Server.'pg-backup-api')
--config-file/-c <config_file> (Path to the agent configuration file.)
asheshvashi@pem:~/PEM/agent$ ./pemworker --register-barman --help
./pemworker --register-barman [barman-registration-options]
barman-registration-options:
--api-url <url> (URL of the BARMAN API 'pg-backup-api')
--description <name> (Description to show on the UI 'User interface' for the BARMAN API.)
--probe-execution-frequency <interval> (Default: 30, Probe the BARMAN API 'pg-backup-api' at regular interval 'in seconds' and fetch the metrics.)
--heartbeat-interval <interval> (Default: 10, Ping the BARMAN API 'pg-backup-api' 'status' API at a regular interval 'in seconds' for checking its availability.)
--ssl-crt <certificate_file> (SSL certificate file for the BARMAN API.)
--ssl-key <key_file> (Private SSL key for the BARMAN API.)
--ssl-ca-cert <ca_file> (CA certificate to verify peer against the BARMAN API.)
--team <database-role> (Specify the name of the database group role, on the PEM backend database server, that should have access to this BARMAN API Server.)
--owner <database-user> (Specify the name of the database user, on the PEM backend database server, who will own the BARMAN API Server.)
--config-file/-c <config_file> (Path to the agent configuration file.)Note
After registering the Barman server, you need to restart the PEM agent.
Viewing the Barman server details on a PEM dashboard
Once the Barman server is configured, you can see the entire backup- and server-related details for that Barman server on the PEM dashboard.
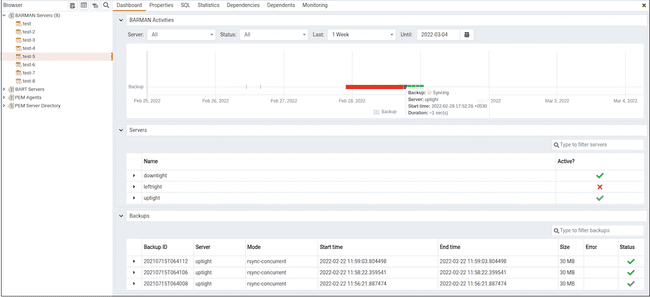
When you select a monitored Barman server, details of all the associated database servers along with their activities are displayed as a chart on the dashboard in the Barman Activities panel. You can select the activities on any criteria that you specify in the filter boxes (the database server, status, duration, or date).
The Servers panel displays a list of all the database servers managed by that Barman server along with the active status.
The Backups panel displays a list of all the database server backups managed by that Barman server. You can filter the list to display the details of any database server. You can also filter the list on any criteria that you specify in the filter box. Typically, this filter works with any kind of string value (excluding date, time, and size) listed under the columns. For example, you can enter tar to filter the list and display only those backups that are in tar format.
Backup details include the Backup ID, Server, Mode, Start time, End time, Size, Error, and Status column.