Moving the PEM server v9
You can move a PEM server from one host machine to a new host machine. The PEM server on the new host (the target) must be installed with the same version of the PEM server installer as the original host (the source). If you don't use the same installer version, you might encounter a schema-mismatch error.
The backend database of the target server (either PostgreSQL or EDB Postgres Advanced Server) can have the same type and version or a different type and version from the backend database of the source PEM server. You can migrate a PEM server that resides on a PostgreSQL host to an EDB Postgres Advanced Server host and vice versa.
Before starting the server migration, make sure that the firewalls between the source host, the target host, and the host of any PEM agent allows connections between the services.
Prepare the target host.
Invoke the installer for the PEM server on the target host. You must use the same version of the PEM server installer that you used when installing the source PEM server.
The backend database of the target server can have a different version or type from the backend database of the source. If the new PEM server doesn't reside on the same type of backend database as the original server, you must ensure that the same version of the sslutils extension is installed on the new server host. The version of sslutils that's distributed with the PEM installers is freely available for download from the EDB website.
For information about installing the PEM server or the sslutils extension, see the PEM installation steps.
Drop existing schemas from the new PEM server.
The migration process re-creates the
pem,pemdata, andpemhistoryschemas from the source PEM server on the target PEM server. To prepare for the move, use the psql client to delete these schemas from thepemdatabase on the target host. You can open the psql client at the command line or by selecting Postgres Enterprise Manager > SQL Shell (psql).When the psql client opens, connect to the
pembackend database as the database superuser. After connecting to thepemdatabase on the target host, drop the schemas:DROP SCHEMA pem CASCADE; DROP SCHEMA pemdata CASCADE; DROP SCHEMA pemhistory CASCADE;
When dropping the schemas, you must include the
CASCADEkeyword, instructing the server to delete all dependent objects. When executing the command, the psql client displays a list of the dependent objects. The client confirms each the schema is removed by displayingDROP SCHEMA.Prepare the PEM agents on the new PEM server.
Before moving the PEM server, you must identify the number of agents that are monitored by the source PEM server and create identities for that number of agents, less one, on the target server. To discover the total number of PEM agents monitored by the PEM server, connect to the
pemdatabase on the source host with the psql client, and query thepem.agenttable.SELECT id FROM pem.agent WHERE active = true;
You must manually create the number of agents that reside on the original PEM server, less one. (The PEM server installer creates one agent on the target host.) For example, if the source server contains three agents, you must manually create two more agents. Open a psql session with the
pemdatabase on the target server, and create the required agents:CREATE USER agent<X>;
Where
<X>specifies an agent number.agent1is created on the target host by the PEM server installer.Then, use the
GRANTcommand to assign each agent that resides on the target PEM serverpem_agentpermissions:GRANT pem_agent TO agent<X>;
Where
<X>specifies an agent number.Generate a backup script of the source PEM server.
You can use the pg_dump utility to generate a script that contains the commands required to re-create the
pemdatabase on the target host. By default, pg_dump is installed in thebindirectory under your Postgres installation. To invoke pg_dump, in thebindirectory, enter:pg_dump -U <user_name> <db_name> > <file_name>
Where:
<user_name>specifies the name of the database superuser for the PEM backend database.<db_name>specifies the name of the PEM backend database.<file_name>specifies the name of the script generated by pg_dump.
When prompted, provide the password associated with the user specified.
The command shown instructs pg_dump to generate a script that, when executed, re-creates the
pemdatabase. The script is namedbackup.sqland is created in thetmpdirectory. pg_dump is connecting to the server using the credentials of the user postgres.Invoking the pg_dump utility doesn't interrupt current database users.
Note
If the source PEM server is earlier than the 7.16 version, then you need to replace the following functions before you run pg_dump to take backup:
- The
abstime,reltime, andtintervaldatatypes are deprecated from Postgres version 12 or later. To replace those dataypes withtimestamptzdata type, use this command:
DO $$ DECLARE rec record; cnt integer; BEGIN -- Check for the deprecated type in our user info probe SELECT count(*) INTO cnt FROM pem.probe_column WHERE sql_data_type = ‘abstime’ AND internal_name = ‘valuntil’; IF cnt = 0 THEN RETURN; END IF; ALTER TABLE pemdata.user_info ALTER COLUMN valuntil SET DATA TYPE timestamptz; ALTER TABLE pemhistory.user_info ALTER COLUMN valuntil SET DATA TYPE timestamptz; -- Now update the pem.probe_column itself UPDATE pem.probe_column SET sql_data_type = ‘timestamptz’ WHERE sql_data_type = ‘abstime’ AND internal_name = ‘valuntil’; END; $$ LANGUAGE ‘plpgsql’;
- Replace the this function to avoid any alert errors:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION pem.check_alert_params_array_size( template_id pem.alert_template.id%type, params text[] ) RETURNS bool AS $FUNC$ DECLARE res bool := TRUE; BEGIN /* * During restoring the pem database, it does not maintain the order while * inserting data in the table, and uses the sort table based on the * names. * Hence - we need to check the foreign key constraint is present before * validating these values. */ IF EXISTS( SELECT 1 FROM information_schema.table_constraints WHERE constraint_name='alert_template_id_fkey' AND table_name='alert' AND table_schema='pem' ) THEN /* * Need to use the IS TRUE construct outside the main query, because * otherwise if there's no template by that ID then the query would return * 0 rows and the result of the function would be undefined and CHECK * constraint would succeed. * Probably this is being over-cautious, because pem.alert.template_id * references pem.alert_template.id. But the SQL standard (probably) does * not define the order in which the CHECK or the FOREIGN KEY constraints * should be validated; in case CHECK is validated first, we want it to * fail. */ EXECUTE $SQL$ SELECT ( SELECT pem.check_array_size_equal(t.param_names, $2) FROM pem.alert_template AS t WHERE id = $1 ) IS TRUE $SQL$ INTO res USING template_id, params; END IF; RETURN res; END $FUNC$ LANGUAGE 'plpgsql';
Move the backup to the target host.
Move the script generated by the pg_dump utility to the target host of the PEM server.
Restore the backup on the target host.
On the target host, in the
bindirectory under the Postgres backend database installation directory, start psql, executing the script generated by the pg_dump utility:psql -U <user_name> -d pem -f <file_name>
Where:
<user_name>specifies the name of the database superuser. The user specified must have connection privileges for the backend database.<file_name>specifies the complete path to the backup script generated by pg_dump.
When prompted, provide the password associated with the database superuser.
The example shown uses the psql client to invoke a script named
backup.sqlto recreate thepemdatabase. The script is invoked using the privileges associated with the database superuser postgres.Stop the database server on the target host.
To stop the PEM server on CentOS or RHEL 7.x or 8.x, use the command:
systemctl stop <service_name>
Where
<service_name>specifies the name of the backend database server. For a PostgreSQL backend database, the service name ispostgresql-<x>. For an EDB Postgres Advanced Server backend database, the service name isedb-as-<X>, where<X>specifies the version number.If you're using Windows, you can use the Services dialog box to control the service. To open the Services dialog box, from the Control Panel, select System and Security > Administrative Tools. Double-click the Services icon. In the Services dialog box, select the service name in the list, and select Stop.
Copy the certificate files to the target host.
You must replace the certificate files that are created when the target host is installed with the certificate files of the source host. Copy the following files from the source PEM server to the target PEM server:
ca_certificate.crtca_key.keyroot.crtroot.crlserver.keyserver.crt
Copy the files to the
datadirectory under the Postgres installation that provides the backend database for the target cluster.On Linux, the files reside in:
/var/lib/pgsql/<X>/data/
On Windows, the files reside in:
C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\<X>\data
Where:
<X>specifies the version of PostgresSQL on your system.The files already exist on the target cluster. Delete the existing files before performing the copy, or overwrite the existing files with the files from the source server. Once in place on the target server, the files must have the platform-specific permissions shown.
On Linux
File name Owner Permissions ca_certificate.crt postgres -rw------- ca_key.key postgres -rw------- root.crt postgres -rw------- root.crl postgres -rw------- server.key postgres -rw------- server.crt postgres -rw-r--r-- On Linux, the certificate files must be owned by postgres. Use the following command to modify the ownership of the files:
chown postgres <file_name>
Where
file_namespecifies the name of the certificate file.Only the owner of the
server.crtfile can modify the file, but any user can read it. Use the following command to set the file permissions for theserver.crtfile:chmod 644 server.crt
Only the owner of the other certificate files can modify or read the files. Use the following command to set the file permissions:
chmod 600 <file_name>
Where
file_namespecifies the name of the file.On Windows
On Windows, the service account that performed the PEM server and backend database installation on the target host must own the certificate files moved from the source host. If you invoked the PEM server and Postgres installer using Run as Administrator from the installer context menu, the owner of the certificate files is Administrators.
To review and modify file permissions on Windows, right-click the file name and select Properties. On the Security tab, select a group or user name to view the assigned permissions. Select Edit or Advanced to open dialog boxes that allow you to modify the permissions associated with the selected user.
Move the PEM agent certificate files to the PEM server host.
You must move the certificate files used by the PEM agent of the source PEM server to the target host. This step is platform specific.
On Linux
Copy the
agent1.keyandagent1.crtfiles from the source host to the target host. By default, on Linux, the files are installed in/root/.pem. Copy the files to the same directory on the target host.File ownership and permissions of the files must be set to:
File name Owner Permissions agent1.key root -rw------- agent1.crt root -rw-r--r-- If necessary, navigate to
/root/.pem, and use the following commands to modify the permissions and ownership of theagent1.keyfile:chmod 600 agent1.key chown root agent1.key
Use the following commands to modify the permissions and ownership of the
agent1.crtfile:chmod 644 agent1.crt chown root agent1.crt
On Windows
Copy the
agent1.keyandagent1.crtfiles from the source host to the target host. On Windows, the files are located in:C:\Users\<user_name>\AppData\Roaming\pem
Where
user_nameis the name of the user that invoked the PEM installer.The ownership and permissions associated with the certificate files on the target machine must match the ownership and permissions of the certificate files on the source machine. If you invoked the PEM server and Postgres installer using Run as Administrator on the installer context menu, the owner of the agent certificate files is Administrators.
To review and modify file permissions on Windows, right-click the file name and select Properties. On the Security tab, select a group or user name to view the assigned permissions. Select Edit or Advanced to open dialog boxes that allow you to modify the permissions associated with the selected user.
Update the
pg_hba.conffiles on the target host.Modify the
pg_hba.conffile on the target host to allow connections from each PEM agent. By default, thepg_hba.conffile is located in the data directory under your Postgres installation.Start the server on the target host.
After modifying the
pg_hba.conffile, you must restart the server for the changes to take effect.To restart the database server on Linux, use the command:
/etc/init.d/<service_name> start
Where
service_nameis the name of the backend database server.On Windows, you can use the Services dialog box to control the service. To open the Services dialog box, on the Control Panel, select System and Security > Administrative Tools. Double-click the Services icon. When the Services dialog box opens, select the service name in the list, and start the service.
Connecting monitored agents to the new PEM server host.
To instruct existing PEM agents to connect to the new PEM server host, you must:
- Ensure that the PEM agent host can connect to the new PEM server host.
- Modify the registry on each Windows host with a PEM agent or the agent configuration files on each Linux host with a PEM agent, specifying the IP address and port of the new PEM server.
- Restart the PEM agent's service. These steps are platform specific:
If the PEM agent resides on Linux
Use your choice of editor to modify the
agent.cfgfile, specifying the new IP address and port number of the PEM server in thepem_hostandpem_portparameters.By default, the
agent.cfgfile is located in:/usr/edb/pem/agent/etc/agent.cfg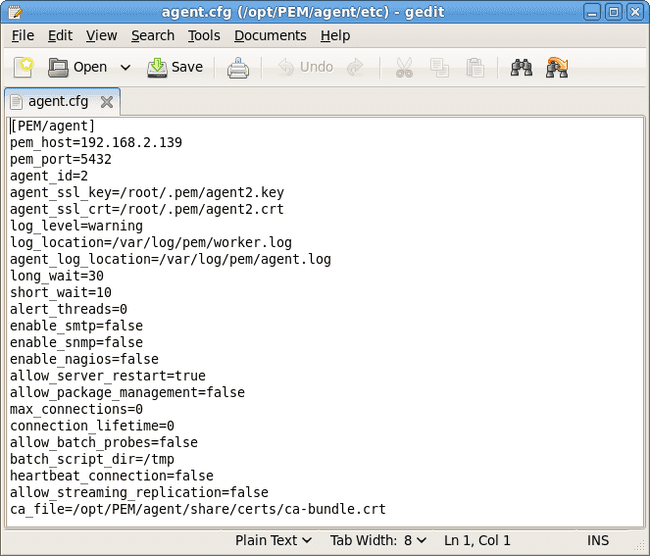
After modifying the
agent.cfgfile, you must restart the PEM agent service. You can use thepemagentservice script on the Linux command line to restart the service:/etc/init.d/pemagent restart
If the PEM agent resides on Windows
Before modifying the Windows registry on the monitored node, confirm that the firewall on the host of the PEM agent allows connections to the PEM server. After confirming that the PEM agent host can connect to the PEM server host, you can use the Windows Registry Editor to review and edit the
PEM_HOSTandPEM_PORTentries to ensure that they correctly identify the host and port used by the PEM server. To open the Registry Editor, enterregeditin the Windows Run dialog box or in the Windows start menu search box. Navigate through the registry tree control to view or modify registry entries.On 64-bit Windows, the PEM agent registry entries are located at:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE SOFTWARE wow6432Mode EnterpriseDB PEM AgentOn 32-bit Windows, the PEM agent registry entries are located at:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE SOFTWARE EnterpriseDB PEM AgentThe
PEM_HOSTandPEM_PORTentries must specify the address and port number of the new PEM server on the target host. To modify a registry entry, right-click the entry name and select Modify from the context menu. Then use the Edit String dialog box to make any changes to the value of the entry. After you finish, select OK.After modifying the registry, you must restart the PEM agent's service. You can use the Services dialog box, accessed through the Windows Control Panel, to restart the
Postgres Enterprise Manager - pemagentservice.After moving the server, change the connection properties in any installed PEM clients to connect to the new host of the PEM server, agents, and monitored servers.
Note
After moving the server, if you encounter this error while creating the server in the PEM web interface:
Error - User does not have enough permission to add new server.
Please contact the administrator to grant 'pem_database_server_registration' role
to the 'enterprisedb' user.Resolve the error by updating the roles and granting appropriate permissions:
UPDATE pem.roles SET rolid = pr.oid FROM pg_roles pr WHERE pr.rolname = 'pem_' || component;