Notifications v9
PEM can send a notification or execute a script if an alert is triggered or cleared. You can send notifications using the following options:
- SMTP
- Webhooks
- SNMP
- Nagios
Use the Notification tab to specify PEM behavior when an alert is raised.
SMTP
You must configure the PEM server to use an SMTP server to deliver email before PEM can send email notifications.
Creating an email group
PEM monitors your system for conditions that require attention. You can use an email group to specify the email addresses of users for the server to notify if current values deviate from threshold values specified in an alert definition. An email group can notify multiple users or target specific users during the time periods you specify.
Use the Email Groups tab to configure groups of SMTP email recipients. To open the Email Groups tab, in the PEM client, select Management > Manage Alerts. When the Manage Alerts tab opens, select Email Groups from the Quick Links toolbar.
The Email Groups tab displays a list of the currently defined email groups. To modify an existing group, select a group name and select Edit at the far left end of the row.
To define a new email group, select the plus sign (+) in the upper-right corner of the Email Groups table. Use the Email Groups dialog box to define an email group and its members.
Each row in the email group definition associates a set of email addresses with a specific time period. When an alert is triggered, the server evaluates the times specified in each row and sends the message to those group members whose definitions are associated with the time that the alert triggered.
Provide a name for the email group in the Group Name field.
To open the Options tab, select the plus sign (+) in the group members table.
Add the member addresses to receive notifications for the time period specified:
- Enter a comma-delimited list of recipient addresses in the Reply to Addresses field.
- Enter a comma-delimited list of addresses to receive a copy of the email in the CC Addresses field.
- Enter a comma-delimited list of addresses to receive a copy of the email without the knowledge of other recipients in the Bcc Addresses field.
- Enter the email address to send the messages from in the From Address field.
- Use the Subject prefix field to provide a message to add to the start of each subject line when a notification is sent.
- Use the From Time and To Time selectors to specify the time range for notifications to the group members that are identified on this row. Provide these values in the locale of the PEM client host. The PEM server translates the time into other time zones as required.
Select Add to add a row to the table, and specify another time period and the email addresses to notify during those hours.
When you've finished defining the email group, select Save.
After creating the email group, you can use the Manage Alerts tab to set up the notification details for an alert to direct notifications to the group.
Deleting an email group
To delete an email group, in the Email Group table, select the name of the group and select Delete, located to the left of the group name.
The group name appears in the Email Group table in red. Select Save to permanently remove the group from the table.
Webhook
You must configure the PEM Server to use webhooks to receive notification of alert events on threshold value violations in your configured applications.
Creating a webhook
PEM monitors your system for conditions that require user attention. You can use a webhook to create the endpoints to receive a notification if current values deviate from threshold values specified in an alert definition. Based on the events triggered, PEM sends a notification to multiple webhook endpoints or to specific target webhook endpoints.
Use the Webhooks tab to configure endpoint recipients. To open the Webhooks tab, select Management > Manage Alerts. From the Manage Alerts tab, on the Quick Links toolbar, select Webhooks.
The Webhooks tab displays a list of the currently defined recipient applications as endpoints. Select an endpoint and select Edit at the far left end of the row to modify an existing endpoint.
To define a new webhook, select the plus sign (+) in the upper-right corner of the table. You can then use the General tab to define the basic details of the webhook:
- Provide a name for the webhook in the Name field.
- Specify a webhook URL to delever all the notifications to in the URL field.
- Set the request method type used to make the call in the Request Method field: POST or PUT.
- By default, webhooks are enabled. To disable a webhook, set Enable? to No.
Note
The Enable? setting works only if the enable_webhook parameter is set to true in the agent.cfg file. By default, the enable_webhook parameter is set to true only for the agent running on the PEM server host. For all other agents running on other hosts, you need to set it to true manually.
Defining webhook SSL configurations
You can define the webhook SSL parameters in the respective agent configuration file or registry in Windows. You can find the list of webhook SSL parameters in PEM agent configuration parameters. If you add or remove any of the agent configuration parameters, you must restart the agent to apply them.
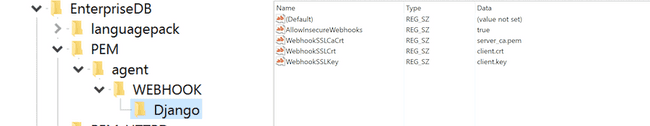
- On 32-bit Windows systems, PEM registry entries for webhooks are located in
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\Software\\EnterpriseDB\\PEM\\agent\\WEBHOOK. - On 64-bit Windows systems, PEM registry entries for webhooks are located in
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\Software\\Wow6432Node\\EnterpriseDB\\PEM\\agent\\WEBHOOK. - On Linux systems, PEM configuration options for webhooks are stored in the
agent.cfg file, located by default in/usr/edb/pem/agent/etc.

Use the HTTP Headers tab to define the header parameters to pass while calling the webhook endpoints:
- Specify all the values as a key and value pair.
- Specify a key parameter in the Key field and a value in the Value field.
- To add HTTP headers, select the plus sign (+) in the upper-right corner of the HTTP Headers table.
- To delete HTTP headers, select Delete to the left of Key. The header remains in the list but in strike-through font. Select Save to permanently delete the headers.
- To edit the HTTP headers, select Edit to the left of Key.
Use the Payload tab to define the JSON data to send to the endpoint when an alert is triggered:
Type specifies data to send in the format type, that is, JSON.
Use Template to configure JSON data sent to endpoints. In the template, you can use placeholders for the following:
%AlertID%— The id of the triggered alert.%AlertName%— The name of the triggered alert.%ObjectName%— The name of the server or agent on which the alert was triggered.%ObjectType%— The type on which the alert was generated.%ThresholdValue%— The threshold value reached by the metric when the alert triggered.%CurrentValue%— The current value of the metric that triggered the alert.%CurrentState%— The current state of the alert.%OldState%— The previous state of the alert.%AlertRaisedTime%— The time that the alert was raised or the most recent time that the alert state changed.%AgentID%— The id of the agent by which the alert was generated.%AgentName%— The name of the agent by which the alert was generated.%ServerID%— The id of the server on which the alert was generated.%ServerName%— The name of the server on which the alert was generated.%ServerIP%— The ip or address of the server on which the alert was generated.%ServerPort%— The the port of the server on which the alert was generated.%DatabaseName%— The name of the database on which the alert was generated.%SchemaName%— The name of the schema on which the alert was generated.%PackageName%— The name of the package on which the alert was generated.%DatabaseObjectName%— The name of the database object, like table name or function name, on which the alert was generated.%Parameters%— The list of custom parameters used to generate the alert.%AlertInfo%— The detailed database object-level information of the alert.
Select Test Connection to test notification delivery to the mentioned endpoint.
Use the Notifications tab to specify an alert level for webhook endpoints:
- Set All alerts to Yes to enable all alert levels to send notifications.
- To send a notification when a specific alert level is reached, set the slider next to an alert level to Yes. You must set All alerts to No to configure an individual alert level.
Deleting a webhook
To mark a webhook for deletion, in the Webhooks table, select the webhook name and select Delete to the left of the name. The alert remains in the list but in strike-through font.
Delete is a toggle. You can undo the deletion by selecting Delete a second time. Select Save to permanently delete the webhook definition.
SNMP
You must configure the PEM server to send the notifications to an SNMP trap/notification receiver before notifications can be sent. Set the SNMP ver to v1, v2, or v3 to identify the SNMP version.
Example - Configure SNMP V3 traps with net-snmp trap receiver
Set
snmp_security_engine_idtoPEM_SNMP_AGENTin plain text format in the Server Configuration dialog box.Convert the plain text value to hexadecimal format to use it in
snmptrapd.conffile. (You can have hexadecimal values ofsnmp_security_engine_idup to 32 octets length).echo PEM_SNMP_AGENT | hexdump -v -e '/1 "%02X"' 50454D5F534E4D505F4147454E540A
Set the following parameters in the Server Configuration dialog box:
- snmp_security_nam to pem_snmp_user
- snmp_authentication_protocol to MD5
- snmp_authentication_password to pem_auth_pass
- snmp_privacy_protocol to DES
- snmp_privacy_password to pem_priv_pass
The
snmptrapd.conffile has the following values:createUser -e 0x50454D5F534E4D505F4147454E540A pem_snmp_user MD5 pem_auth_pass DES pem_priv_pass authUser log pem_snmp_user
Using PEM with Nagios
The PEM server can send a passive alert result to Nagios network-alerting software when a user-defined alert is triggered. To instruct the PEM server to notify Nagios of a triggered alert, you must:
- Enable Nagios notification for each alert that triggers a notification from the PEM server to Nagios. You must configure PEM alerting before you create the
host.cfgandservices.cfgfiles. - Configure Nagios-related behaviors of the PEM server.
- Create the
host.cfgandservices.cfgconfiguration files. - If necessary, modify the Nagios configuration file and restart the Nagios server.
- Install the PEM agent on the system where the Nagios server is installed and register it with the PEM Server. Set
enable_nagiosconfiguration totruein theagent.cfgfile for that agent, and restart the agent service.
After configuring the server to enable Nagios alerting, any triggered alerts send a passive check result to the Nagios service. The syntax of a passive alert is:
<timestamp> PROCESS_SERVICE_CHECK_RESULT; <host_name> ; <service_name> ; <service_status> ;
Where:
timestamp is the date and time that the alert was triggered.
host_name is the name of the server or agent.
service_name is the name of the alert.
service_status is the numeric service status value:
- 0 if the service status is OK
- 1 if the service status is WARNING
- 2 if the service status is CRITICAL
- 3 if the service status is UNKNOWN
The PEM server uses the following rules to evaluate the service status:
- If the PEM alert level is CLEARED, the warning message reads OK.
- If the PEM alert level is LOW, the warning message reads WARNING.
- If the
is_nagios_medium_alert_as_criticalflag (specified in the PEM server configuration dialog box) is set to FALSE and the alert level MEDIUM, the warning message reads WARNING. - If the
is_nagios_medium_alert_as_criticalflag (specified in the PEM server configuration dialog box) is set to TRUE and the alert level is MEDIUM, the warning message reads CRITICAL. - If the PEM alert level is HIGH, the warning message reads CRITICAL.
Enabling Nagios notification for an alert
The PEM server maintains a unique set of notification properties for each enabled alert. Use the Notification tab of the Manage Alerts tab to specify that, when triggered, a given alert sends an alert notice to Nagios.
To modify the notification properties of an alert, right-click the name of the object monitored by the alert, and select Management > Manage Alerts. On the Manage Alerts tab, select Edit to the left of the alert name in the Alerts list. When the edit pane opens, select the Notification tab.
To enable Nagios notification, move the slider next to Submit passive service check result to Nagios to Yes. Then select Save.
Configuring Nagios-related behavior of the PEM Server
You can use the Server Configuration dialog box to provide information about your Nagios configuration to the PEM server. To open dialog box, select Management > Server Configuration.
Four server configuration parameters specify information about your Nagios installation and PEM server behavior related to Nagios:
Use the
nagios_cmd_file_nameparameter to specify the location of the Nagios pipeline file that receives passive check alerts from PEM. The default value of this parameter is/usr/local/nagios/var/rw/nagios.cmd. If yournagios.cmdfile resides elsewhere, specify the file location in the Value field.Move the slider in the
nagios_enabledparameter to Yes to instruct the PEM server to send passive check alerts to Nagios.Use the
nagios_medium_alert_as_criticalslider to specify the warning severity that the PEM server passes to Nagios if a medium alert is triggered:If the
is_nagios_medium_alert_as_criticalflag is set to FALSE and the alert level is MEDIUM, the warning message reads WARNING.If the
is_nagios_medium_alert_as_criticalflag is set to TRUE and the alert level is MEDIUM, the warning message reads CRITICAL.
Use the
nagios_spool_retention_timeparameter to specify the number of days of notification history to store on the PEM server. The default value is 7 days.
After modifying parameter values, select Save in the upper-right corner of the dialog box.
Creating the hosts.cfg and services.cfg file
The templates.cfg file (by default, located in /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects) specifies the properties of a generic host and generic service. The properties specify the parameters used in the hosts.cfg and services.cfg files.
In most cases (when PEM is installed in a default configuration), you don't need to modify the templates.cfg file before creating the hosts.cfg and services.cfg files. If necessary, you can modify the templates.cfg file to specify alternative values for parameters or to create new templates.
Before modifying the Nagios configuration file, use the following command to create a hosts.cfg file that contains information about the PEM hosts that reside on the local system:
psql -U postgres -p 5433 -d pem -A -t -c "select pem.create_nagios_host_config('generic-host')" > /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/hosts.cfg
Then, use the following command to create a services.cfg file that contains information about the PEM services that reside on the local system:
psql -U postgres -p 5433 -d pem -A -t -c "select pem.create_nagios_service_config('generic-service')" > /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/services.cfg
If you want to use a custom template.cfg file entry, specify the entry name in place of generic-host or generic-service in these commands.
Modifying the Nagios configuration file
After creating the host.cfg and services.cfg files, you must specify their location in the Nagios configuration file (by default, /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg). Modify the configuration file, adding entries that specify the location of the files:
cfg_file=/usr/local/etc/objects/hosts.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/etc/objects/services.cfg
You can use the following command to confirm that Nagios is properly configured:
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
After confirming that Nagios is configured correctly, restart the Nagios service:
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
- On this page
- SMTP
- Webhook
- SNMP
- Using PEM with Nagios