Exploring conflict handling with PGD v5
Conflicts
A multi-master architecture like PGD will see conflicts happen. PGD is built to handle them.
A conflict can occur when one database node has an update from an application to a row and another node has a different update to the same row. This is called a row level conflict. Conflicts aren't errors and effectively resolving them is core to how Postgres Distributed maintains consistency.
The best way to handle conflicts is to not have them in the first place! Use PGD's Always-On architecture with proxies to ensure that your applications write to the same server in the cluster.
When there are conflicts though, it is useful to know what PGD does to resolve them, how you can control that resolution and how you can find out that they are happening. This topic explores two ways in which conflicts can be caused: row insertion and row updates.
To see how it works, you need to open a command line view of all the servers.
Your quick started configuration
This exploration assumes that you created your PGD cluster using the quick start for Docker or the quick start for AWS.
At the end of both those quick starts, you'll have a cluster with four nodes and these roles:
| Host name | Host role |
|---|---|
| kaboom | PGD data node and pgd-proxy co-host |
| kaftan | PGD data node and pgd-proxy co-host |
| kaolin | PGD data node and pgd-proxy co-host |
| kapok | Barman backup node |
You'll use these hostnames throughout this exercise.
Installing xpanes
You'll use xpanes, a utility that allows you to quickly create multiple terminal sessions that you can easily switch between. It isn't installed by default, so you'll have to install it. Start by connecting to the kaboom node with ssh.
cd democluster && ssh -F ssh_config kaboom
If you're running the quick start on Docker, you'll be using Rocky Linux, a Red Hat derivative. To perform the xpanes install, run:
dnf -y install xpanes
If you're running the quick start on AWS, you'll be using Debian Linux. To perform the xpanes install, run:
wget https://github.com/greymd/tmux-xpanes/releases/download/v4.1.4/tmux-xpanes_v4.1.4.deb sudo apt -y install ./tmux-xpanes*.deb rm tmux-xpanes*.deb
Connecting to four servers
You need to be logged in as the enterprisedb user to allow authentication to work:
sudo -iu enterprisedb
Then, run the following command to connect to three database servers and a proxy server:
xpanes -d -c "psql postgresql://enterprisedb@{}/bdrdb?sslmode=require" "kaboom:5444" "kaftan:5444" "kaolin:5444" "kaboom:6432"
xpanes takes the command after -c and uses the values in the arguments that follow to create a command to run. That means that, after you run it, there will be four panes. Three panes will be connected to the database nodes kaboom, kaftan, and kaolin on port 5444. One will be connected to the pgd-proxy running on kaboom on port 6432. Each one will be logged into the database as enterprisedb.
Press Control-b followed by q to briefly display the numeric values for each pane.
To switch the focus between the panes, you can use Control-b and the cursor keys to navigate between them. Or you can use Control-b followed by q and the number of the pane you want to focus on. We'll show both ways.
Move to the bottom-left pane using Control-b ↓ Control-b → or Control-b q 3**.
Preparing for conflicts
To make a conflict, you first need a simple table. In the pane that currently has focus, enter:
drop table if exists test_conflict; create table test_conflict( id integer primary key , value_1 text);
Monitoring conflicts
In the pane that currently has focus, enter:
select * from bdr.conflict_history_summary \watch 1
The select command displays the conflict history for the cluster. The \watch 1 command is a psql command that reruns the preceding command every second.
You are now ready to generate a conflict.
Creating a conflict
The most basic form of conflict is when an insert happens to a table on two different nodes and both have the same primary key. You can now create that scenario and observe it.
Move to the top-left pane using Control-b ↑ Control-b ← or Control-b q 0. This pane is the kaboom node. Start a transaction there, and insert a row:
start transaction; insert into test_conflict values (1, 'from kaboom');
Next, move to the top-right pane using Control-b → or Control-b q 1. This pane is the kaftan node. Here, you'll also start a transaction and insert into the same row with different data.
start transaction; insert into test_conflict values (1, 'from kaftan');
You now have two transactions open on different servers, with an insert operation already performed successfully. You need to commit both transactions at this point:
- Use Control-b ← or Control-b q 0, and then enter
commit;. - Use Control-b → or Control-b q 1, and then enter
commit;.
You'll see that both commits are working. However, in the bottom-right pane, you can see the conflict being detected.
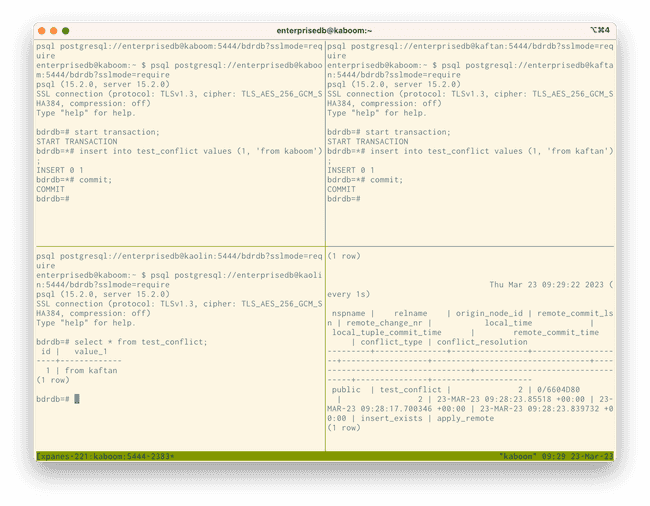
A row in the conflict history now notes a conflict in the table where the insert_exists. It also notes that the resolution for this conflict is that the newer record, based on the timing of the commit, is retained. This conflict is called an INSERT/INSERT conflict. You can read more about this type of conflict in INSERT/INSERT conflicts.
Creating an update conflict
When different updates to the same records take place on different nodes, a conflict occurs. You can create that scenario with the current configuration, too. Leave \watch 1 running in the bottom-right pane.
Move to the top-left pane using Control-b ← or Control-b q 0. This pane is the kaboom node. Here, start a transaction and update a row:
start transaction; update test_conflict set value_1 = 'update from kaboom' where id = 1;
Next, move to the top-right pane using Control-b → or Control-b q 1. This pane is the kaftan node. Here, also start a transaction, and update the same row with different data:
start transaction; update test_conflict set value_1 = 'update from kaftan' where id = 1;
You now have two transactions open on different servers, with an update operation already performed successfully. You need to commit both transactions at this point:
- Use Control-b cursor-left or Control-b q 0, and then enter
commit;. - Use Control-b cursor-right or Control-b q 1, and then enter
commit;.
Again you'll see both commits working. And, again, in the bottom-right pane, you can see the update conflict being detected.
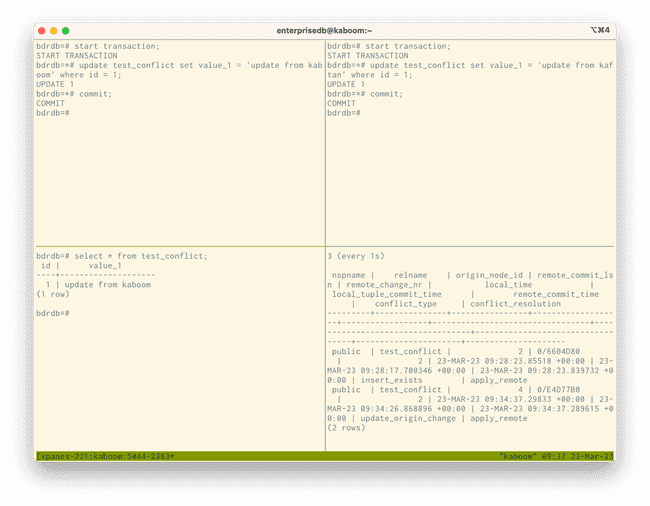
An additional row in the conflict history shows an update_origin_change conflict occurred and that the resolution was apply_remote. This resolution means that the remote change was applied, updating the record. This conflict is called an UPDATE/UPDATE conflict and is explained in more detail in UPDATE/UPDATE conflicts.
Other conflicts
You are now equipped to explore all the possible conflict scenarios and resolutions that can occur. For full details of how conflicts are managed, see Conflicts in the documentation. While ideally you should avoid conflicts, it's important to know that, when they do happen, they're recorded and managed by Postgres Distributed's integrated and configurable conflict resolver.