Benchmarking v1
The CNP kubectl plugin provides an easy way for benchmarking a PostgreSQL deployment in Kubernetes using EDB Postgres for Kubernetes.
Benchmarking is focused on two aspects:
IMPORTANT
pgbench and fio must be run in a staging or pre-production environment. Do not use these plugins in a production environment, as it might have catastrophic consequences on your databases and the other workloads/applications that run in the same shared environment.
pgbench
The kubectl CNP plugin command pgbench executes a user-defined pgbench job on an existing Postgres Cluster.
The command also accepts the --dry-run flag, this will output the job manifest without applying it.
Example usage:
kubectl cnp pgbench \ -n <namespace> <cluster-name> \ --pgbench-job-name <pgbench-job> \ --db-name <db-name> \ -- --time 30 --client 1 --jobs 1
Example of how to run pgbench against a Cluster named cluster-example in the pgbench namespace:
kubectl cnp pgbench \ -n pgbench cluster-example \ --pgbench-job-name pgbench-job \ -- --time 30 --client 1 --jobs 1
Example of how to run pgbench on an existing database by using the --db-name flag and
the pgbench namespace:
kubectl cnp pgbench \ -n pgbench cluster-example \ --db-name pgbench \ --pgbench-job-name pgbench-job \ -- --time 30 --client 1 --jobs 1
The job status can be fetched by running:
kubectl get job/pgbench-job -n <namespace> NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE pgbench-job-name 1/1 15s 41s
Once the job is completed the results can be gathered by executing:
kubectl logs job/pgbench-job -n <namespace>
fio
The kubectl CNP plugin command fio executes a fio job with default values and read operations.
The command also accepts a --dry-run flag, this will output the fio manifest without applying it.
Note
The kubectl plugin command fio will create a deployment with predefined fio job values using a ConfigMap.
If you want to provide custom job values, we recommend generating a manifest using the --dry-run flag
and providing your custom job values in the generated ConfigMap.
Example usage:
default
kubectl cnp fio <fio-name>
with values
kubectl cnp fio <fio-name> \ -n <namespace> \ --storageClass <name> \ --pvcSize <size>
Example of how to run the fio command against a StorageClass named standard and pvcSize: 2Gi in the fio
namespace:
kubectl cnp fio fio-job \ -n fio \ --storageClass standard \ --pvcSize 2Gi
The deployment status can be fetched by running:
kubectl get deployment/fio-job -n fio NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE fio-job 1/1 1 1 14s
After running kubectl plugin command fio.
It will:
- Create a PVC
- Create a ConfigMap representing the configuration of a fio job
- Create a fio deployment composed by a single Pod, which will run fio on
the PVC, create graphs after completing the benchmark and start serving the
generated files with a webserver. We use the
fio-toolsimage for that.
The Pod created by the deployment will be ready when it starts serving the results. You can forward the port of the pod created by the deployment
kubectl port-forward -n <namespace> deployment/<fio-name> 8000
and then use a browser and connect to http://localhost:8000/ to get the data.
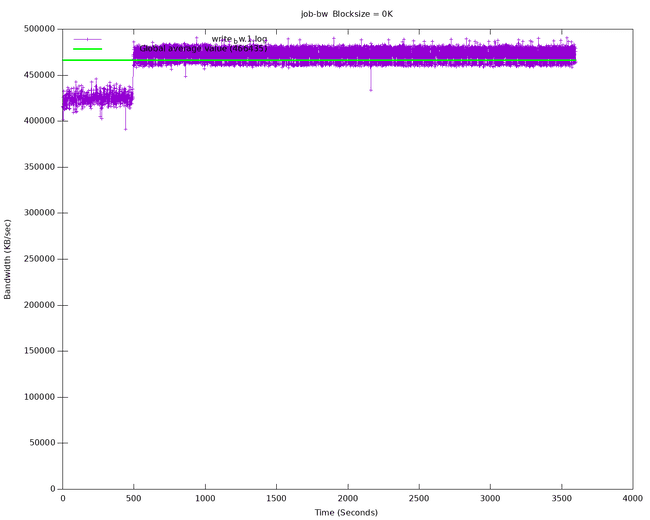
The default 8k block size has been chosen to emulate a PostgreSQL workload. Disks that cap the amount of available IOPS can show very different throughput values when changing this parameter.
Below is an example diagram of sequential writes on a local disk mounted on a dedicated Kubernetes node (1 hour benchmark):
After all testing is done, fio deployment and resources can be deleted by:
kubectl cnp fio <fio-job-name> --dry-run | kubectl delete -f -
make sure use the same name which was used to create the fio deployment and add namespace if applicable.