Transparent Data Encryption
Transparent data encryption (TDE) is an optional feature supported by version 15 of EDB Postgres Advanced Server and EDB Postgres Extended Server with high availability.
It encrypts any user data stored in the database system. This encryption is transparent to the user. User data includes the actual data stored in tables and other objects as well as system catalog data such as the names of objects.
What's encrypted with TDE?
TDE encrypts:
The files underlying tables, sequences, indexes, including TOAST tables and system catalogs, and including all forks. These files are known as data files.
The write-ahead log (WAL).
Various temporary files that are used during query processing and database system operation.
Implications
Any WAL fetched from a server using TDE, including by streaming replication and archiving, is encrypted.
A physical replica is necessarily encrypted (or not encrypted) in the same way and using the same keys as its primary server.
If a server uses TDE, a base backup is automatically encrypted.
The following aren't encrypted or otherwise disguised by TDE:
Metadata internal to operating the database system that doesn't contain user data, such as the transaction status (for example, pg_subtrans and pg_xact).
The file names and file system structure in the data directory. That means that the overall size of the database system, the number of databases, the number of tables, their relative sizes, as well as file system metadata such as last access time are all visible without decryption.
Data in foreign tables.
The server diagnostics log.
Configuration files.
Implications
Logical replication isn't affected by TDE. Publisher and subscriber can have different encryption settings. The payload of the logical replication protocol isn't encrypted. (You can use SSL.)
How does TDE affect performance?
Performance is in line with the general overhead for AES.
How does TDE work?
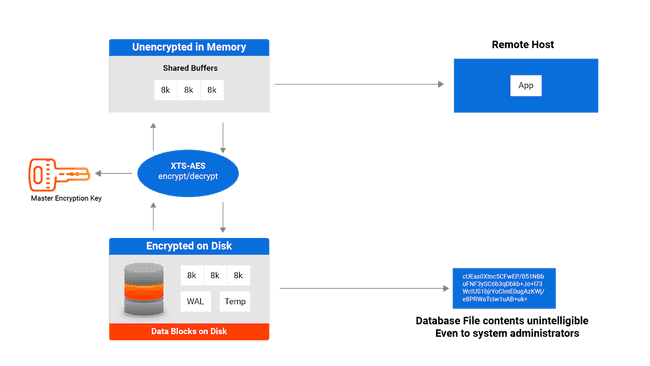
TDE prevents unauthorized viewing of data in operating system files on the database server and on backup storage. Data becomes unintelligible for unauthorized users if it's stolen or misplaced.
Data encryption and decryption is managed by the database and doesn't require application changes or updated client drivers.
EDB Postgres Advanced Server and EDB Postgres Extended Server provide hooks to key management that's external to the database. These hooks allow for simple passphrase encrypt/decrypt or integration with enterprise key management solutions. See Securing the data encryption key for more information.
How does TDE encrypt data?
TDE encrypts the data files using AES-128-XTS. The XTS “tweak” uses the database OID, the relfilenode, and the block number.
The WAL is encrypted using AES-128-CTR. The “counter” includes the WAL LSN.
Temporary files that are accessed by block are also encrypted using AES-128-XTS. Other temporary files are encrypted using AES-128-CBC.
How is data stored on disk with TDE?
In this example, the data in the tbfoo table is encrypted. The pg_relation_filepath function locates the data file corresponding to the tbfoo table.
insert into tbfoo values ('abc','123'); INSERT 0 1 select pg_relation_filepath('tbfoo'); pg_relation_filepath ---------------------- base/5/16416
Grepping the data looking for characters doesn't return anything. Viewing the last five lines returns the encrypted data:
$ hexdump -C 16416 | grep abc $ $ hexdump -C 16416 | tail -5 00001fc0 c8 0f 1d c8 9a 63 3d dc 7d 4e 68 98 b8 f2 5e 0a |.....c=.}Nh...^.| 00001fd0 9a eb 20 1d 59 ad be 94 6e fd d5 6e ed 0a 72 8c |.. .Y...n..n..r.| 00001fe0 7b 14 7f de 5b 63 e3 84 ba 6c e7 b0 a3 86 aa b9 |{...[c...l......| 00001ff0 fe 4f 07 50 06 b7 ef 6a cd f9 84 96 b2 4b 25 12 |.O.P...j.....K%.| 00002000
- On this page
- What's encrypted with TDE?
- How does TDE work?